Module 9 - Advanced Software Features
System Status, Communications & Logs
System Information
The system information tab displays details relating to important components that make up the system. For example, the Linux version or how long is left on the licence.
To access this window, select About from the System tab on the toolbar.
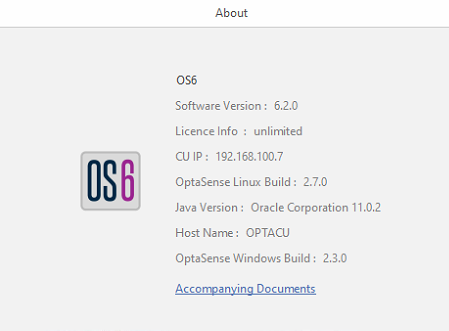
Left: Accessing System information / Right: System Overview Page
System Health & Process Management
System Health
System Health provides the health state of the major processes and interfaces running on the system. To access this window, select System Health from the Process Management tab on the toolbar.
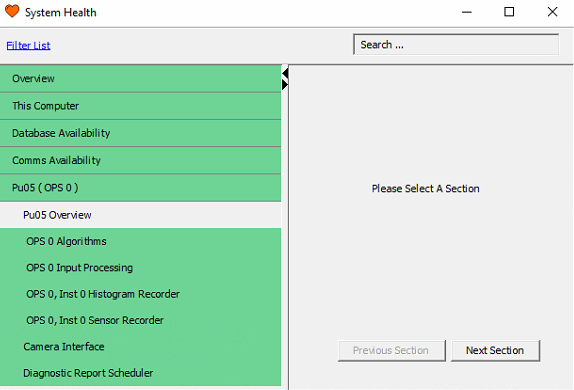
System Health
-
Processes that are running without issue will be highlighted in green
-
Processes that have been intentionally disabled will be highlighted in grey
-
Any processes that are in an error state will be highlighted red.
-
A user notification will occur if a process enters an error state. Below, the histogram recorder can be seen to have entered an error state as a result of the Algorithms process being stopped.
- The user notification can be expanded to provide further details about why an error has occurred.
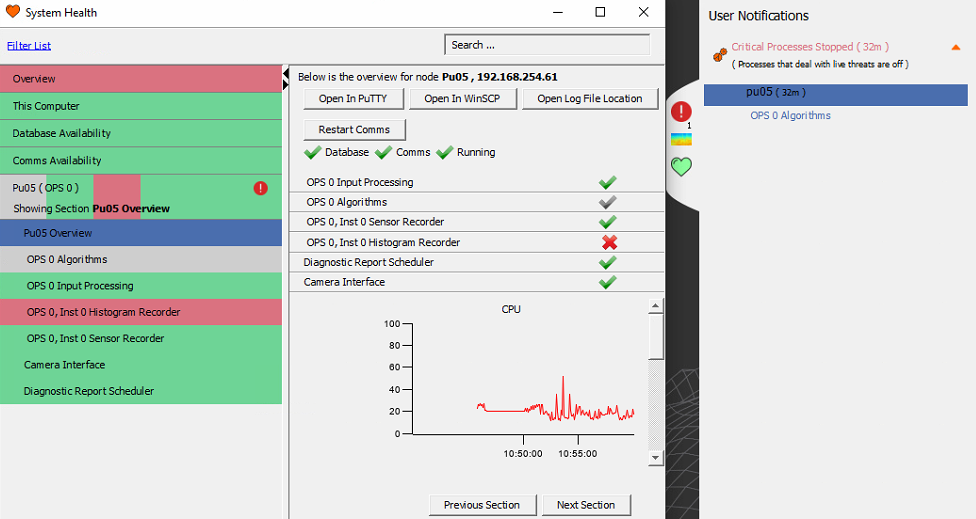
Process / Interface State / User Notifications
Stopping, Starting Processes
All process can be stopped/started via System Health and selecting 'Overview'
It is possible to stop/start processes on a per node basis. This can be achieved by opening the System Health display and selecting a node. All processes for this node can be stopped/started. Below showcases the ways processes can be turned off and on from System Health.
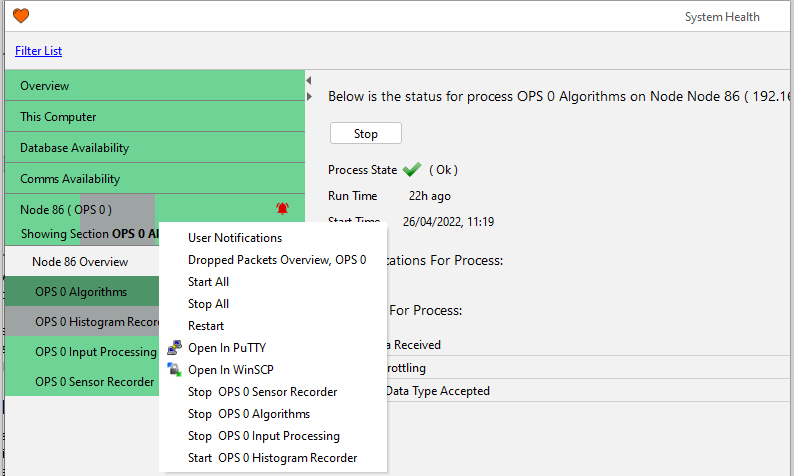
Stop / Start Processes / Interfaces
Node Status Overview
The status overview page displays each processing server (Node) and the status of the processes running on it. To reveal these, click on the required node. Each process can be stopped and restarted in two ways.
-
Right-click on the process and select Stop / Start.
-
Select the process, then Stop / Start from the central window.
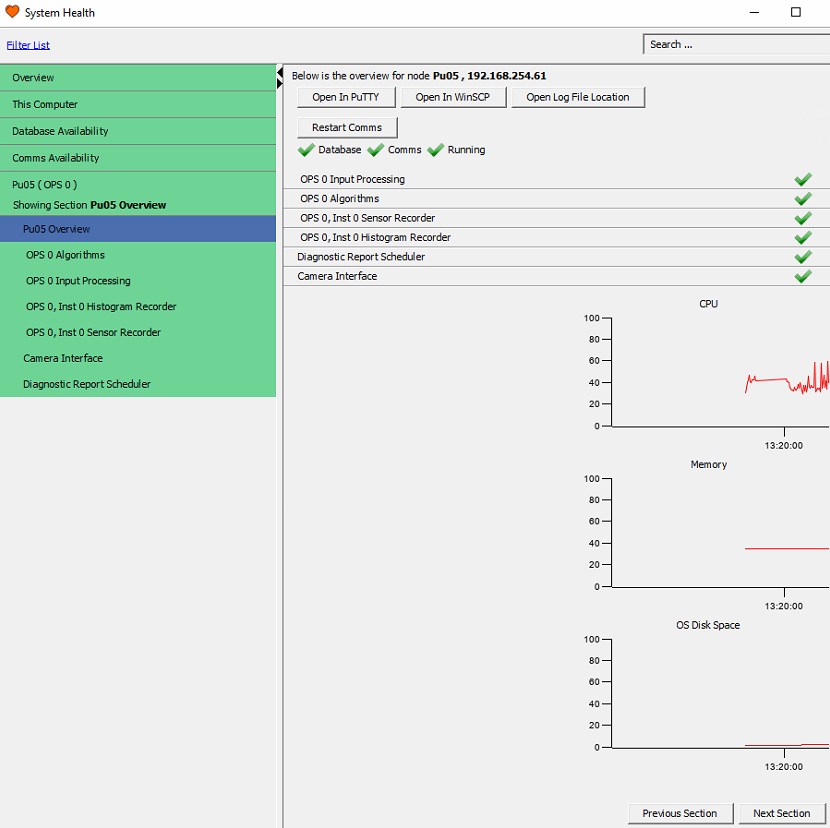
Processing Node Status Overview
Restart Processes Button Overview
For each node, there are corresponding 3rd party tools:
- Open in PuTTY - Utility that provides console access to Linux on the node.
- Open in WinSCP - Utility that provides Linux GUI folder and file navigation on the node.
- Open Log File Location - Displays log files for the node.
- Restart Comms - Restarts Hazelcast on the node.
Database Availability
This section details the connection state of the distributed database. The database view can be expanded or closed by left-clicking on the Database banner. This gives a system overview of the database connections. To access this function, from the toolbar, select Process Management and then System Health.

Expanded Database Availability view
Comms Availability
The section details the communication state of all nodes on the system. The system communication view can be expanded or closed by left-clicking on the system communications banner.

Expanded System Comms Availability view
Global Process Management
Global Process Management enables the user to stop and start important processes collectively across the system. The following list describes those processes.
Restart Processes Button Overview
- Stop / Start All – Restarts all-important processes listed in the System Health.
- Stop / Start Algorithms – Restarts detector algorithm processes.
- Stop / Start Input Processing – Restarts the data stream process from the IUs to the algorithms.
- Stop / Start Sensor Recordings – Restarts the sensor recordings processes.
- Stop / Start Histogram Recordings – Restarts the histogram recordings processes.
- Restart Comms Cluster – Restarts the communication process across all nodes.
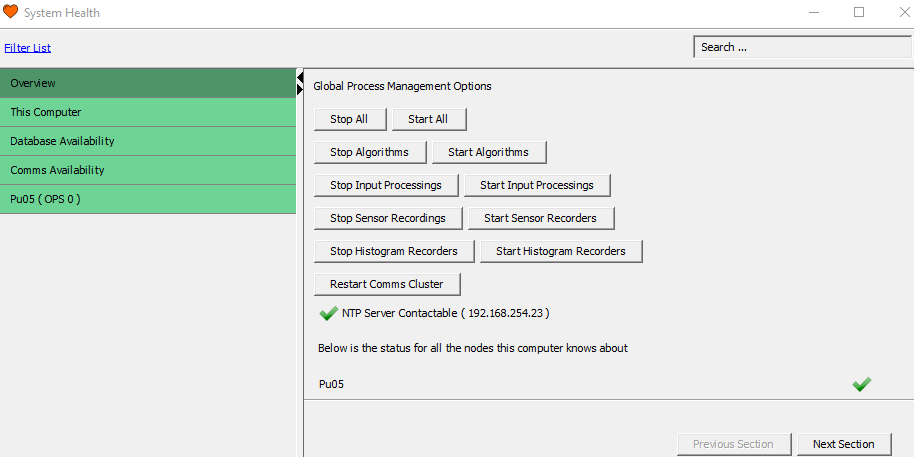
Global Process Management
Dropped Packet
Dropped Packets are an indication that the system is unable to keep up with the data being received. When this happens, an error will appear in the User Notification window. Some examples of causes of drop packets are having too many detectors running simultaneously or if a hard drive is running slowly.
If dropped packets are occurring regularly, an investigation into the cause must be undertaken.
Dropped Packets
Processing Chain Performance
Processing Chain Performance gives a resource overview of all processes running on the system. To access this window, select Processing Performance from the Process Management tab on the toolbar. Values includes:
- The amount of time spent in each processing step
- The current and max watermark levels seen in each of the buffers
- The number of packets that have been lost within a given step
High values can indicate processing strain and packet losses should be investigated.
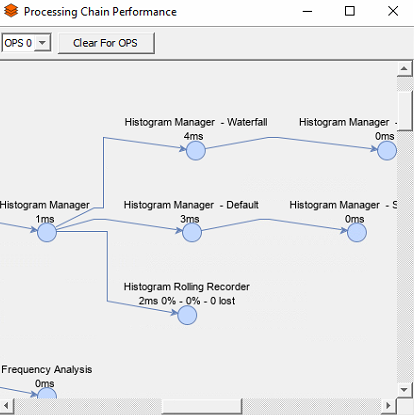
Processing Chain Performance
Historical Analysis
Historic Waterfall Data
The alert history waterfall enables the visualisation of historic data. This can be accessed by typing 'Historic Waterfall Data' or from the toolbar, select the Alert History Waterfall button from the Historical Analysis tab.
Historical Waterfall Data
The dialog box shown will appear where the desired OPS, date/time and channel range can be specified. The data source can also be changed to retrieve data from other rolling recorders. The search function is limited to a 24 hours period.
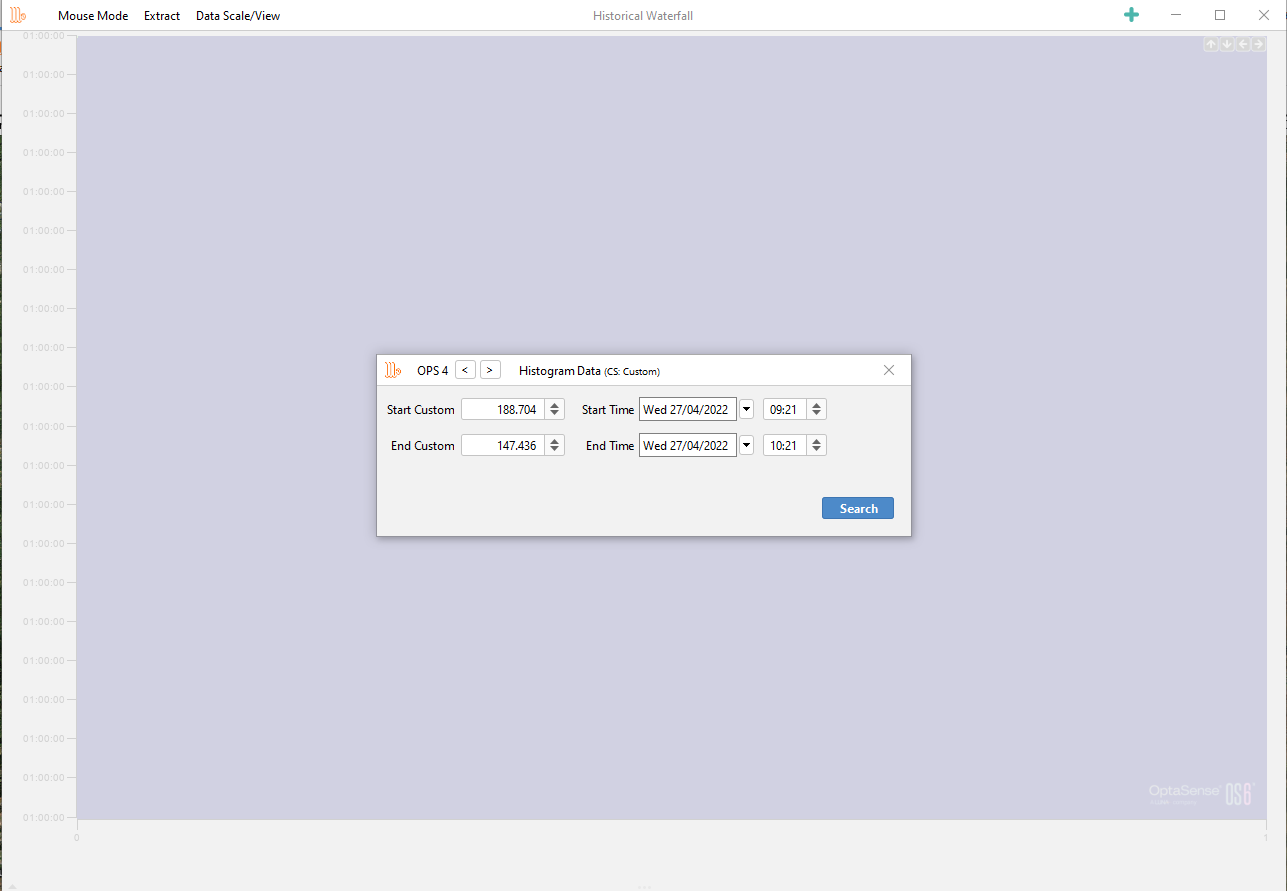
Selecting data based on OPS, date/time & channel range
Assuming the data is available, a snapshot of the data and any associated alerts from within the time span will appear.
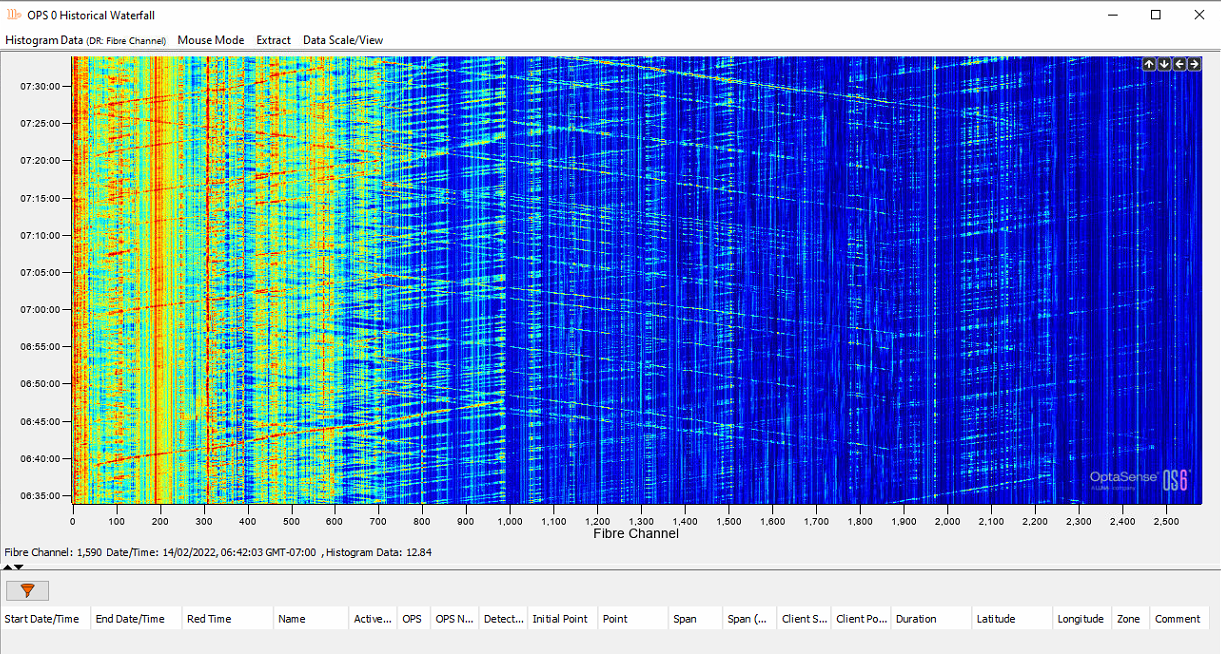
Historic Waterfall
Extracting Data
Data can be extracted from each of the rolling recorders as raw data or to CSV as required. Sensor data can require large amounts of space and the overall file size is limited.

Extracting Sensor Data
Name the data accordingly and choose between copying to Server's Record Location or Copy to CU. When copying to CU, the user will be prompted to choose a storage location.
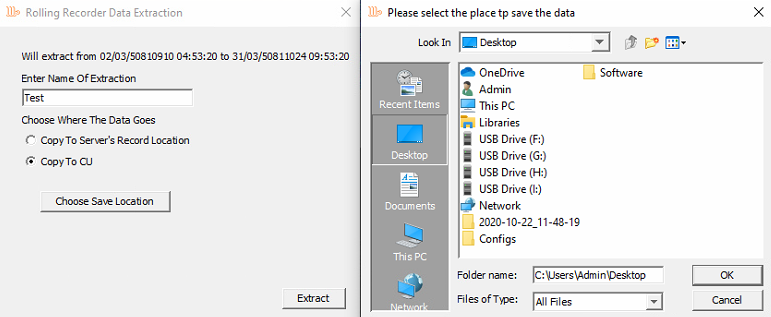
Choosing Storage Location
Copying to Server Record Location will store the data in the same directory as manual recordings. If using a Linux navigation utility, e.g. WinSCP, by default, the storage location is /mnt/disk4/ManualRecord0
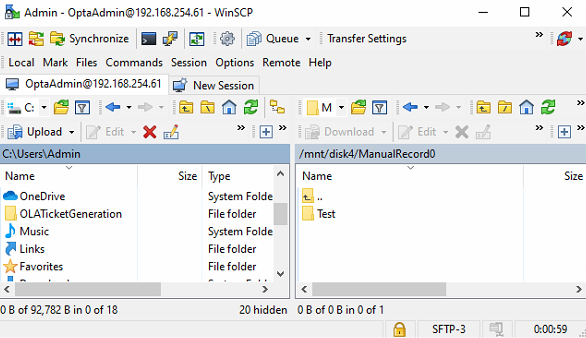
Linux Navigation Utility
Historical Multi-Channel Trending
The historical multi-channel analysis tool enables the user to plot histogram and leak data recorded on the system at a given date/time.
There are 2 ways this feature can be accessed.
- From the toolbar, select Historical Analysis, then Historical Multi-Channel Trending.
- On the OS main window, select the alert list icon (high, medium/low). Now click the required alert, right-click and select Historical Multi-Channel Trending.
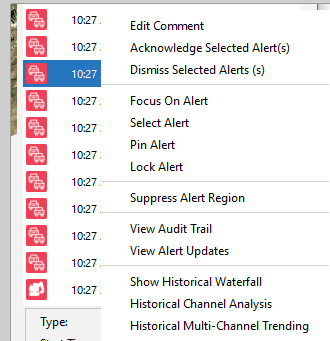
Left - Historical Multi-Channel Analysis / Right - Selecting the Feature from Alert
In the window below, a line graph is plotted outlining the source of data from an alert. To manually choose a source, click Add Source. Scale Options enable the time of the source to be edited. The + button enables another source to be plotted within the same window. The x button removes a source.
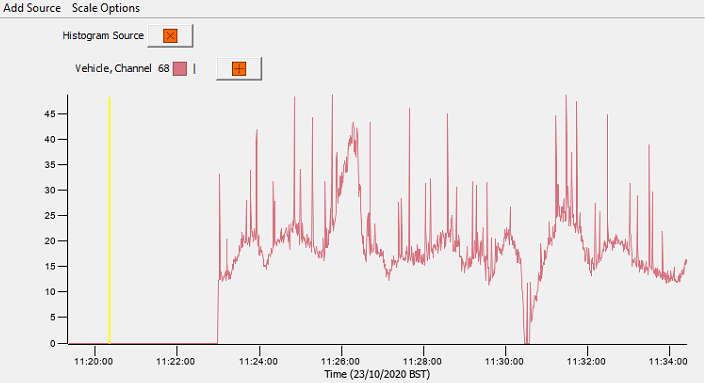
Analysis Options
Historical Alerts
Historical alerts can be displayed. These alerts can then be exported into a chart or CSV format. To access this feature, from the toolbar, select Historical Analysis and then Historical Alerts.
Analysis Options
From the toolbar on the left side, the user can select the duration they require to run the report on. The user can also select the level of alert (low, medium or high), a specific alert type and span the search over multiple OPS. Once this form is filled out, users can either extract the results to CSV/HTML or display the results on the right-hand pane showing all information stored about the occurrences, e.g. start and end channel, type (personnel, vehicle etc.), latitude and longitude and comments entered by the user. This right-hand pane uses a 'Page' mechanism in that users can page through 10000 alerts at a time.
Note the alerts highlighted with colour indicate they haven't been acknowledged by the user.
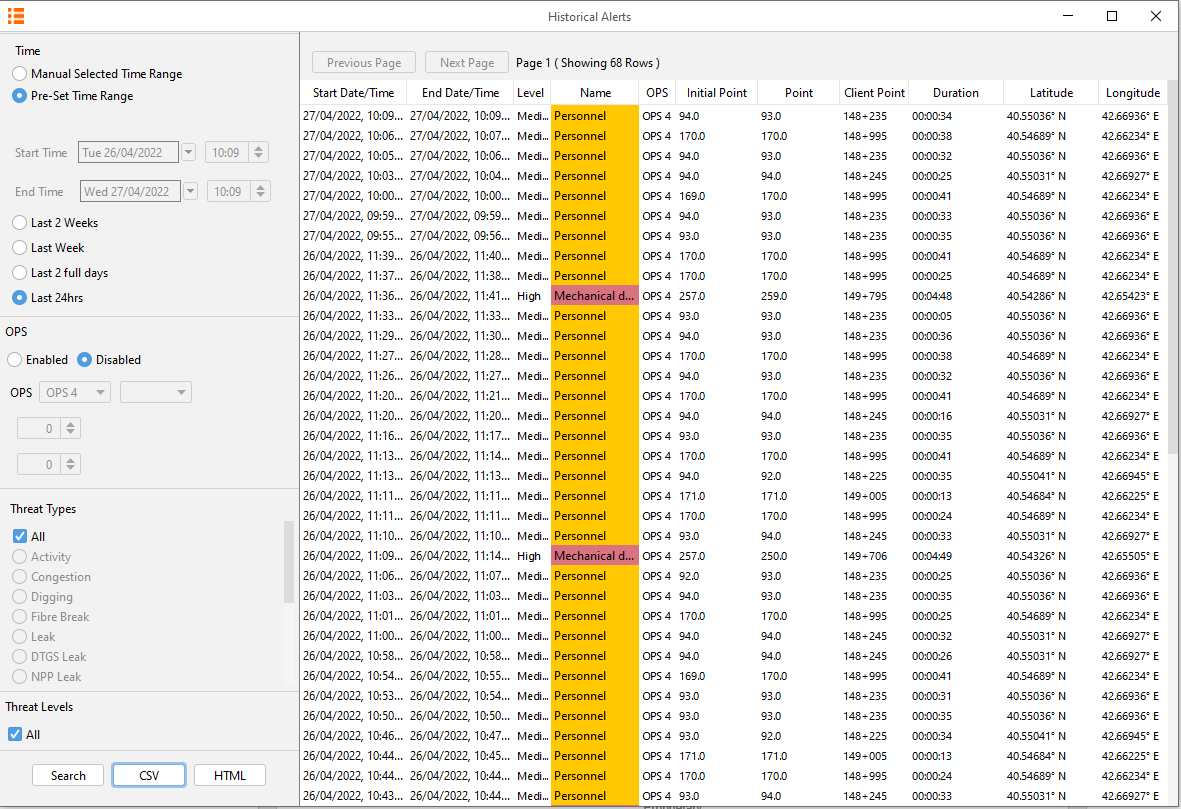
Historical Alert List
Historical Alert Extraction
There are two options for exporting alert data.
The button will export alert data into Microsoft (MS.) Excel file format. Once the button is clicked, a prompt will ask you to confirm the export; select yes. Choose the desired location and click save. Another prompt will appear confirming that the export has finished.
Exporting Alert Search to MS Excel
The button will export the data into web page format. Once the button is clicked, choose the desired location, and select Open. Now select the required charts from the chart option drop-down box or select Add All. Select Generate to compile the report.

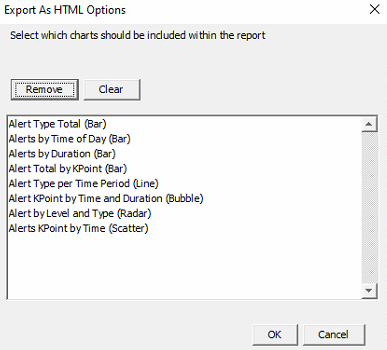
Exporting Alert Search Query to HTML
Once the report has finished, the following prompt will display.

Confirmation of Successful Report Generated
The contents of the zipped file will need to be extracted to view its contents.
Alert Charts
There are three tabs on the top left of the browser.
- Charts - Displays a list of charts
- Waterfall - Provides a histogram waterfall based on the duration selected in the alert search query.
- View - Selecting Default will change the view mode to extended. This provides increased viewing focus on charts. Theme: Changes the white borders of the webpage to grey.
Charts that can be Selected
(Example) Chart Types
Alert Type Total (Bar)
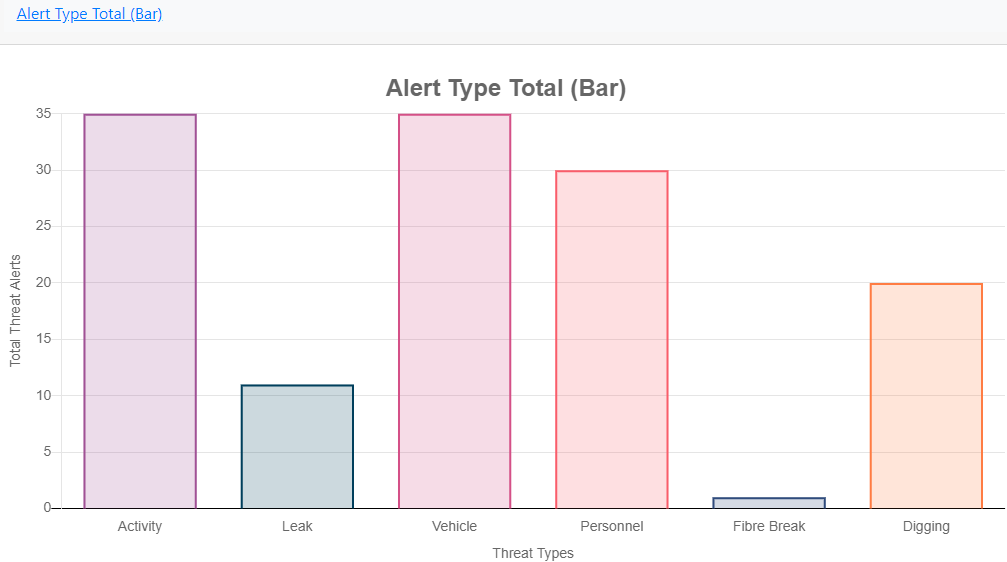
Alert Type Total
Alert KPoint by Time and Duration (Bubble)
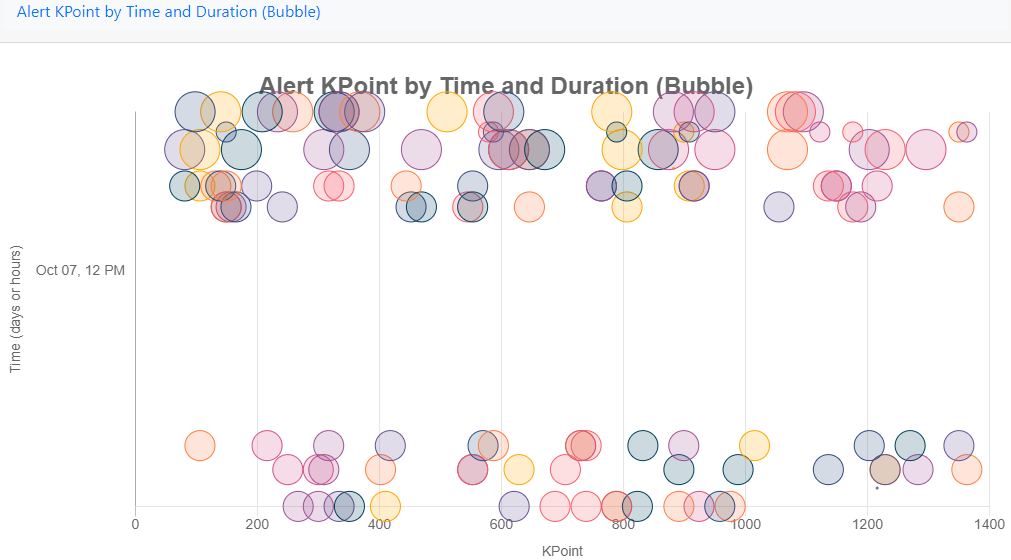
Alert KPoint by Time and Duration
Auditing
Auditing enables the user to view the changes made to the system and by whom. To access this feature, from the toolbar, select Historical Analysis and then Audits.
Audits
From the toolbar on the left the user can select the duration they require to run the audit on. By default, all nodes, actions and by whom they were made by will be selected.
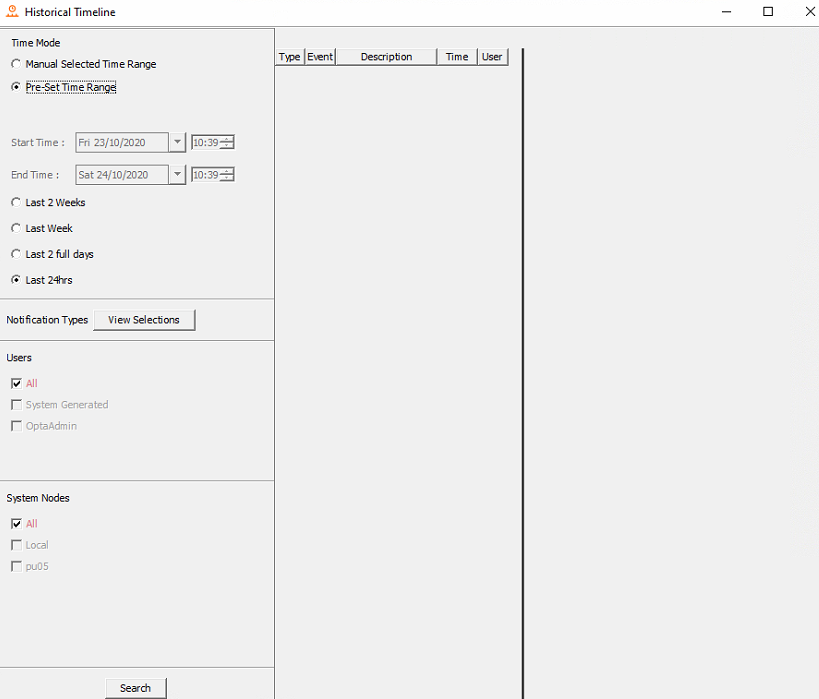
Auditing search dialog
To change what actions are to be listed, select View Selection as shown in the image above. Uncheck the unrequired actions.
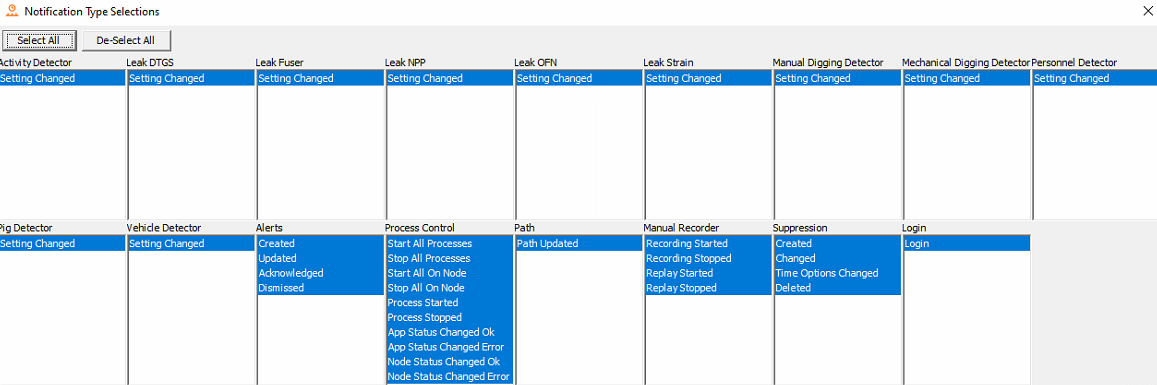
Audit Viewer**
Select search to run the audit. To display more information on an instance, hover over. To quick filter, use the search box and type the name of action / user required. The column headers can also be used to filter. For example, selecting type will order the list of actions by the type of instance.
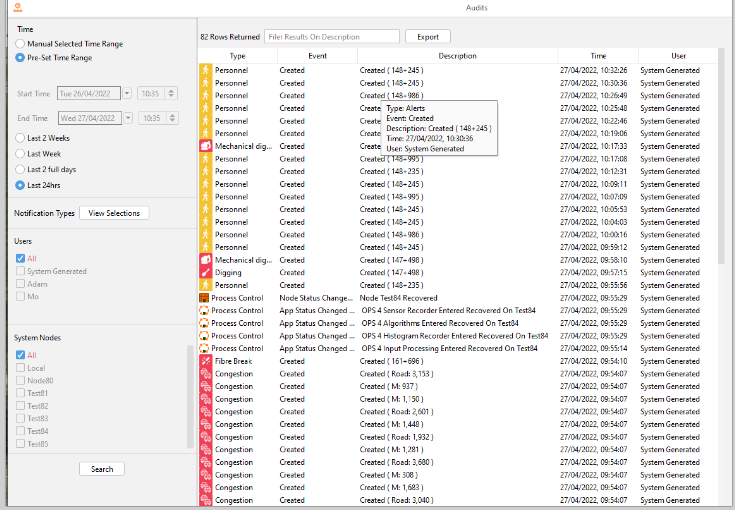
Audits List
Audit Trail
Along with seeing audits in the format seen in below, audit trails/linked audits can also be viewed. Audits that are linked normally share a characteristic like an identifier or name so that the change history for that link can be seen overtime. An example of this is viewing an alerts' audit trail overtime to see when it was created, updated, or acknowledged etc or to see the change history of a Detector setting.
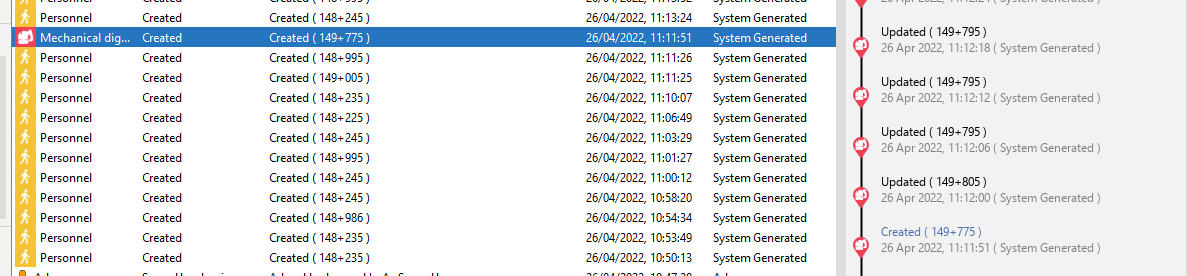
Audit Trail for an audit in the Audit Window
In this display, when a row is selected, the audit trail for that row is shown to the right with the selected row in that trail highlighted in blue.
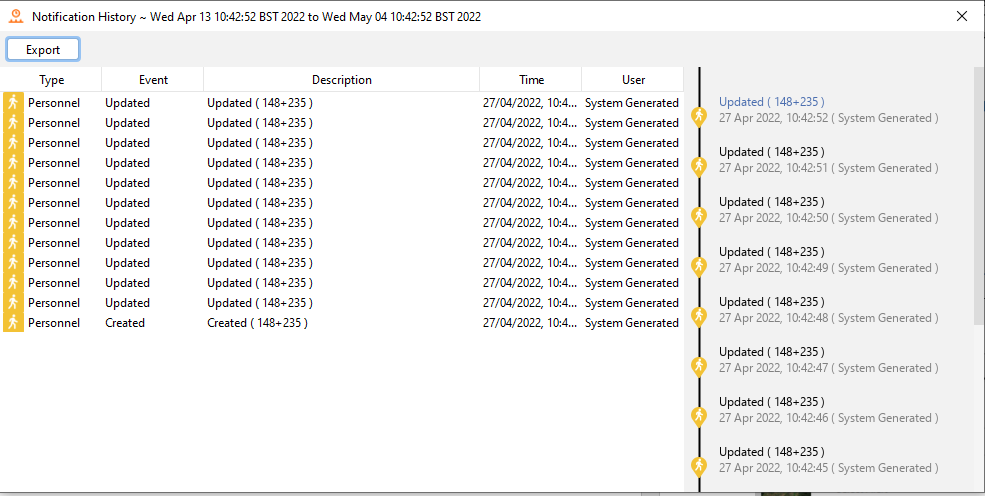
Audit Trail for an audit in the Audit Trail Window
The second way to view the trail for an event is to use 'View Audit Trail' menu seen on the Live Timeline Menu and Alert menu (Totes, Map etc). This option will open a display in which the audit trail will show for the selected event. This display also allows the trail to be exported to csv.
Historical Process Metrics
Process report charting enables the user to select the resources that they want to view:
Memory (%) – Displays the memory usage for the specified process.
CPU (%) - CPU usage for the specified process.
GC Throughput (%) - Amount of time being spent in the Java garbage collector as opposed to time spent running process code. Consistent drops more than a few percent below 100% should be investigated.
GC Pause Time Sec – Time spent by the Java garbage collector freeing temporary memory. The more time spent here, the less time being spent by the CPU running process code. Occasional pauses of one or two seconds are acceptable but long pauses are likely to cause issues.
To access this feature, from the toolbar select Historical Analysis and then Historical Process Metric.
Historical Process Metric
From the toolbar on the left the user must select the required node, monitoring period and what processed are to be displayed as plotted charts. It's advised that continuing spikes, dips, or absent periods be investigated.
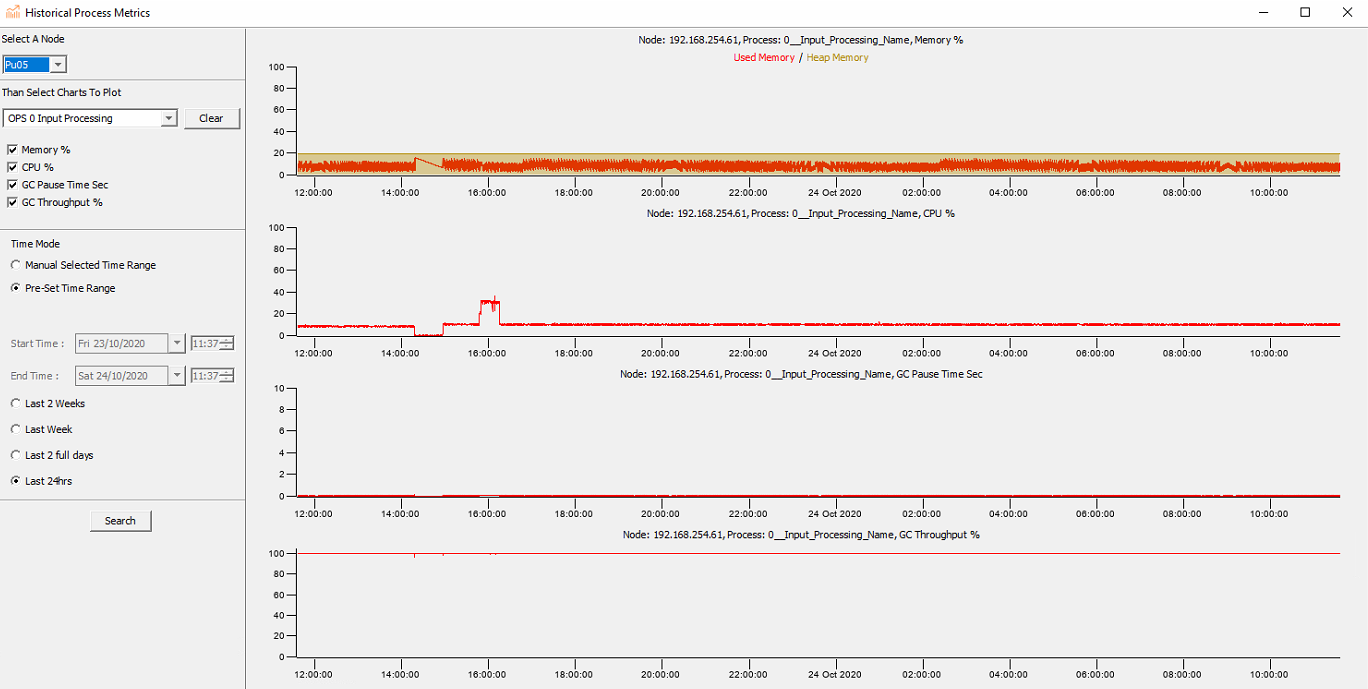
Process Report Charting
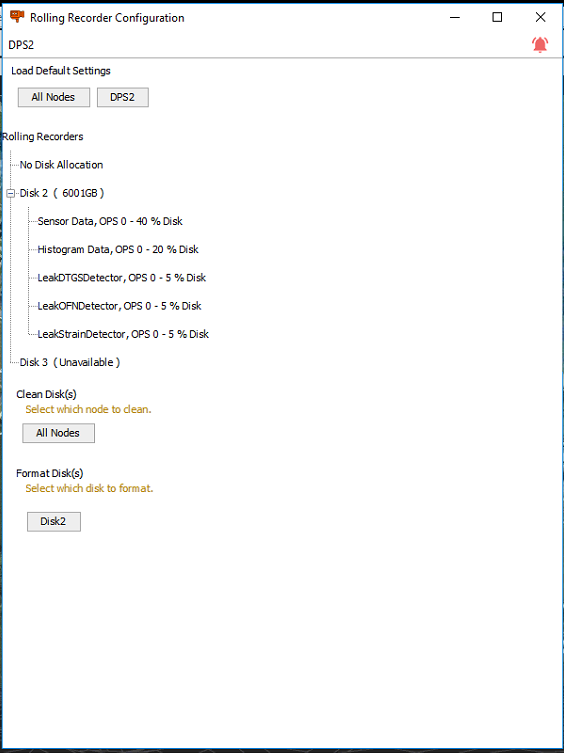
Rolling Recorders
The Rolling Recorders section in the configure tab allows the operator to configure the rolling recorders for the histogram, sensor data, and leak algorithms
The rolling recorder configuration window will show the disk(s) associated to the selected node and show disk allocation associated to each data stream associated to the rolling recorder. The rolling recorder path is set automatically and default settings for storage can be applied per OPS or globally across all nodes.
Rolling Recorder Configuration Screen
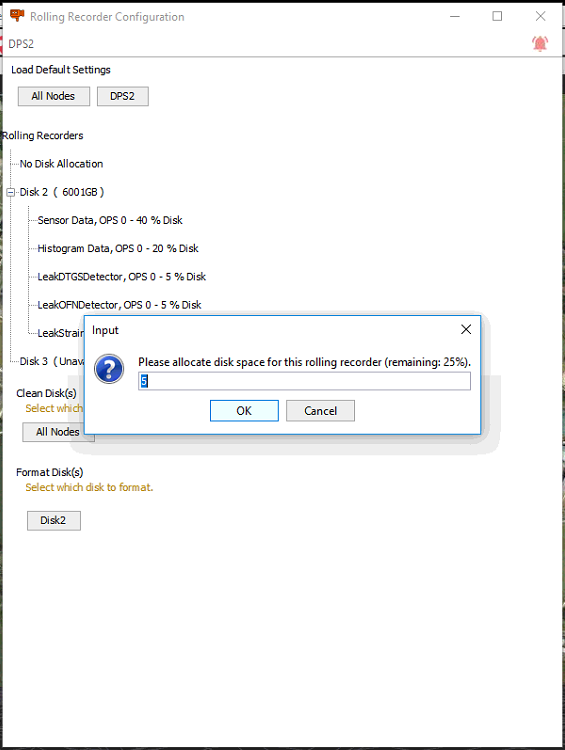
It is possible to change storage allocation to each stream by right clicking a stream and adjusting the allocated storage space, shown as a percentage of the available space on the rolling recorder drive.
Rolling Recorder Storage Allocation
Config Management
The Config Management option in the System tab allows for import and export of config files and folders within the operator software (briefly covered in Module 4: Config Creator).
Import Config allows for the import of either an entire config folder or import of individual config files.
Export Config allows for the export the entire config folder to a target location on the CU.
Export Config
Config files should only be changed by an expert user or after consultation with OptaSense Support. Changes to files may require additional user action to utilise the desired changes and uncontrolled changes may be damaging to the system.
Manipulating Map Screen Artefacts
Fibre Layer
The Configure>Fibre Route panel enables the user to make changes to an existing fibre route. This feature is useful should the physical fibre change geographically or in terms of length.
To open the Fibre Layer Configuration panel, from the toolbar, select Configure and then Fibre Route
Accessing Fibre Route configuration
There are several options the user can use to aid when configuring of the fibre route.
Checking the options numbered below will show the following fibre route display overviews.
- Nodes
- Fibre Route – fibre route in line format
- Channel Coverage
- Calibration Points
- OPS Names – Name of OPS covering a given section on the fibre route.
- Other OPSes – Show all OPSes
- Centre On Map Display view on chosen OPS
- Fibre Color – Color of fibre route.
- OPS Drop Down – Select specific OPS
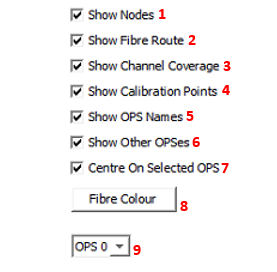
Fibre Route Visual Options
Examples of the more important options applied.
Show Nodes: Green circles mark the fibre route and generally denote a change of direction
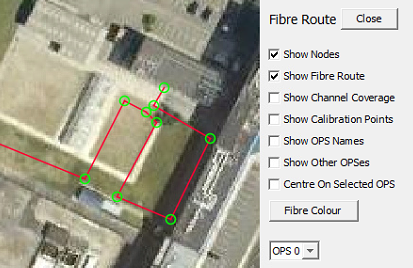
Showing Fibre Nodes
Show Channel Coverage: Blue circles denote the channel coverage selected. Should not overlap or have spaces between them
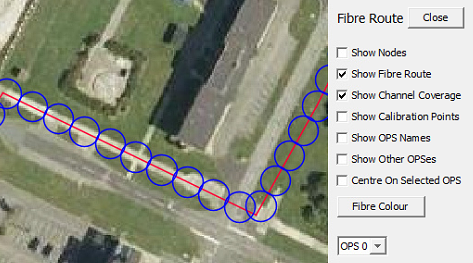
Showing Channel Coverage
Show Calibration Points: Yellow crosses – used to refernce the fibre to the ground and contain position and optical distance information

Showing Calibration Points
- Choose between fibre route node / cal points configuration
- Node and calibration point edit buttons (map window)
- Import fibre route – Refer to Module 4 Config Creator for more information regarding importing fibre routes
- Copy to Cal Point – Takes a selected node point and creates a calibration point. (Note, when using, the user must switch to cal points and configure the additional information required to plot the point).
- Add, delete, edit and reverse change node point.
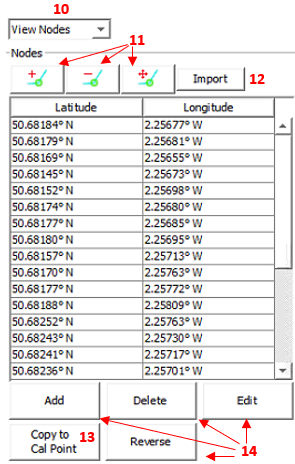
Fibre Route Edit Options
When switching to plotted calibration points, it's good to have a basic understanding of the following numbered points below.
- Switch between displaying calibration points in terms of optical distance along fibre or in fibre channels
- Toggle on and off calibration points. This is useful if the cal point was acting as a place holder.
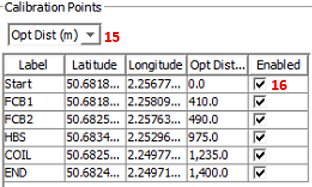
Calibration point Pointers
The user should regularly save their actions as they make changes the fibre configuration. It is advised to save every couple of actions. Should a mistake be made within those actions, the undo button can be used. The button below will appear after any change.
Calibration point Pointers
Nodes
Fibre nodes are generally provided by the client and are imported from a .csv file. Once the fibre layout has been added to the map layer there is usually no requirement to change it. In exceptional circumstances the fibre can be edited with the following buttons:
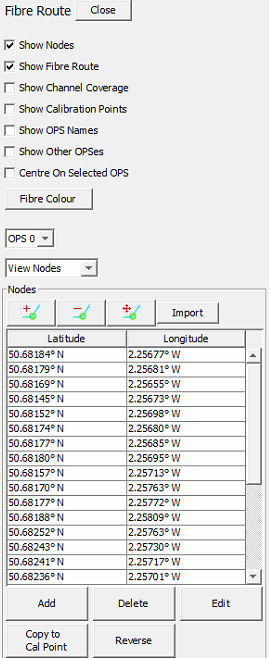  |
|---|
Node Configuration
Channel Coverage and Calibration Points
The channels are represented by blue circles that have the same diameter as the selected channel spacing. Geo-referencing is required to ensure that the length and route of the fibre that has been be placed onto the map layer is correct and accounts for loops of fibre that may be buried in splice chambers, etc. These loops can then be 'compressed' into a single channel enabling accurate alert posting to the map screen. The channel coverage circles are linked directly to the calibration points.
The calibration points contain data about the optical distance between each point as well as a unique name and geographical reference for placement. Right clicking on the desired calibration point will bring up the 'Edit Calibration Point' box. This is where the Optical Distance from the last calibration point can be changed and the Calibration point can be enabled or disabled.
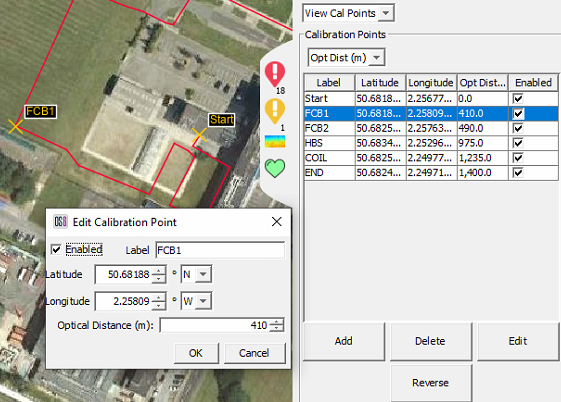
Calibration Point Editingclient
Custom Routes
Paths
Paths can be created on the Map screen to highlight features like roads, tracks, rivers and other geographical markers.
To begin creating a path, select Custom Routes from the Configure tab.

Custom Routes Location
Clicking 'Add' will load the add new custom route dialogue box up an Input box and prompt for a new for the new path. Ensure that the Route Type is set to "Path", enter a path name and click OK. The colour can be changed before selecting OK if desired.
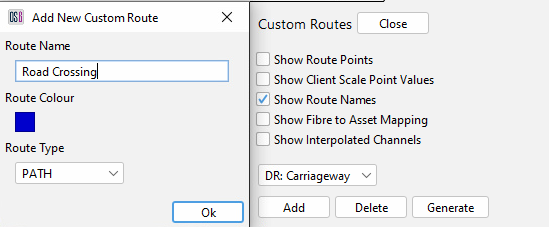
Path creation from custom routes
To start drawing a path, select the Add Route Nodes button in the custom routes dialogue and click on the map display where the first point is positioned. Select a second point, to which a line will be drawn. Additional points can be added between two existing nodes by creating a node close to the line between the two nodes. To remove a point, select the Remove Route Nodes button and click on the required point to delete it. Selecting the Move Route Nodes button allows existing nodes to be manipulated into a different position. Once the path is drawn, either add more custom routes as required or press Close. Pressing Close will open a Save changes prompt where changes can be saved or ignored. If adding multiple routes, it is advisable to save changes regularly.
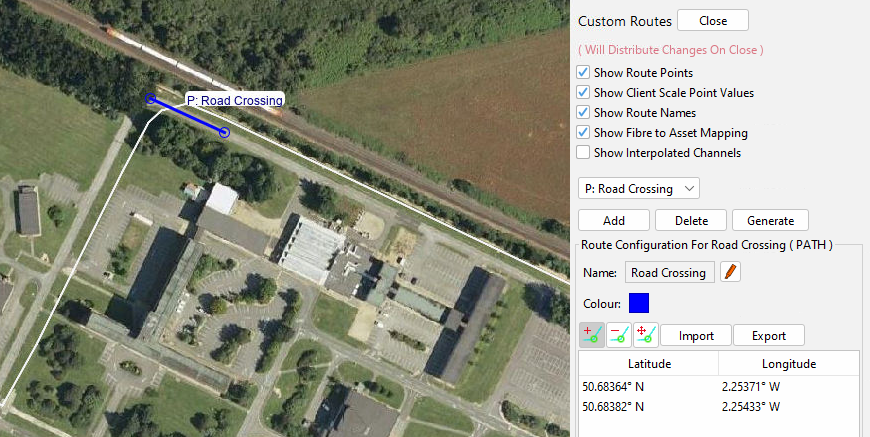
Path on the map display
Asset Route
Asset route mapping allows the operators to create custom routes that can be used within detectors to address the differences between fibre route and asset routes – for instance, the effect of optical coils. Asset routes make use of a 'Fibre to Asset Mapping' algorithm to enable monitoring of an asset in relation to the monitored fibre. Notable examples where this would prove useful would be road and rail assets.
Only the Road Detector can currently make use of Asset Routes.**
To create an Asset Route, select configure custom routes from the toolbar and add a new route. Give the Asset Route a name and ensure that Asset Route is selected in the drop-down menu. An Asset Route will always be mapped to Fibre Channels
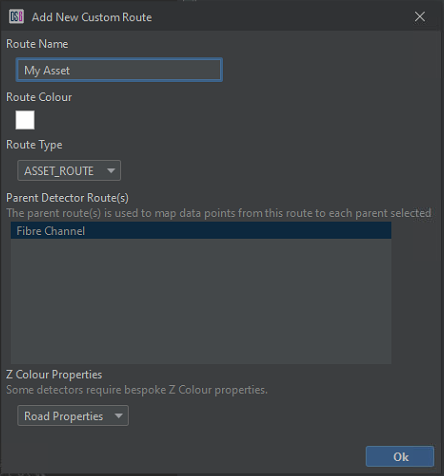
Asset Route Creation
Select OK to create the route. It is then possible to add/remove and move Asset points on the map from the asset dialogue. Once an asset route has been created, if the Show Fibre to Asset checkbox is selected, the interpolated channel mapping to each asset channel is visible (denoted by the short blue lines).
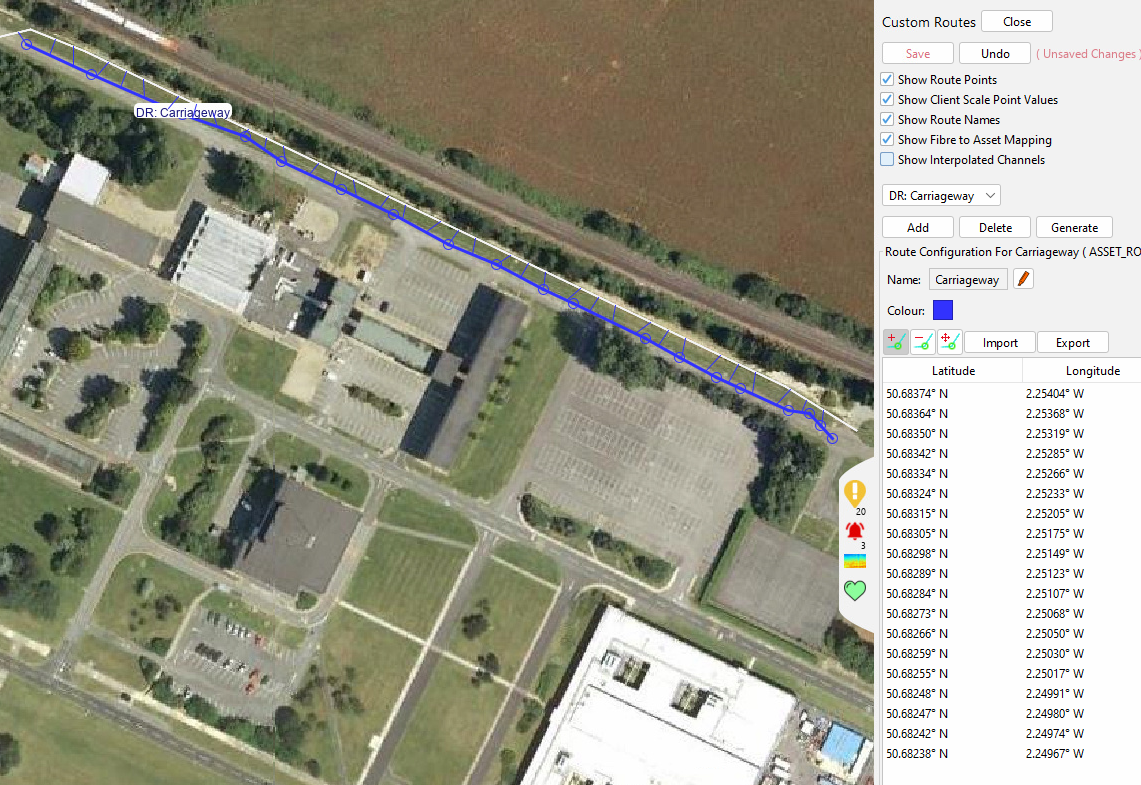
Asset Route showing mapping to OPS channels
Assets can be grouped into ‘Detector Routes’ which consists of Fibre and Asset Routes
Client Scale
The client scale is used to plot a series of reference points along Detector Routes – most commonly K-points along pipelines. A client scale allows alerts to be output with custom markers that the client may be more familiar with. The client scale can also be used on the waterfall display to change the x-axis. When using a client scale on the waterfall display the x-axis will always run increase from left-to-right; The fibre channels will automatically be flipped if the scale runs in the reverse order to the fibre channels. While a Client Scale can span multiple OPS, the waterfall display will only display the section that is relevant to the currently selected OPS.
Utilising a 'Fiber to Asset Mapping' mechanism means it is now possible to create client scales that follow an asset (e.g. a pipeline) rather than the fibre route. This allows unnecessary fibre channels to be removed from the fibre route when displayed on the waterfall (for instance, optical coils or fibre around a block valve station). Multiple Client scales can be created to allow a waterfall to show just the relevant channels for different routes.
Adding a New Client Scale
To add a client scale, open the custom routes dialogue and choose Add. Provide a name for the scale, colour and select Client Scale from the drop-down menu. The table at the bottom allows the selection of different parent routes so that client scales can be mapped to Assets Routes instead of OPS.
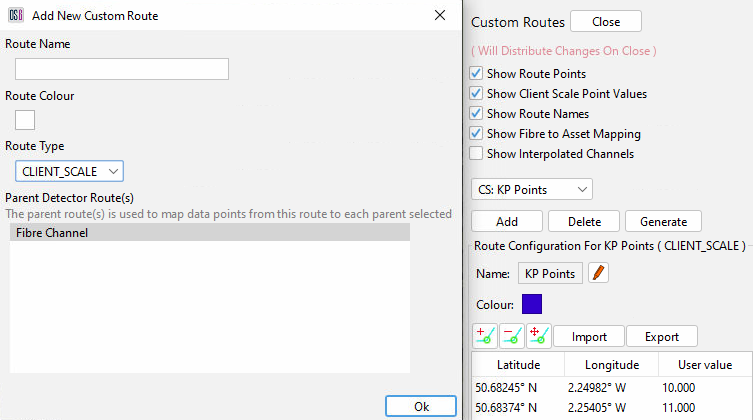
Client Scale
Select OK to create the Client Scale. It is then possible to add, remove and move client scale points on the map. Unique User values must be assigned to each point, and these will be interpolated between pairs of points along the defined route. Checking the 'Show Interpolated Channels' flag will show each client scale channel as a circle along the route. Checking the 'Show Fibre to Asset Mapping' flag will draw lines showing the mapping of each client scale channel to the parent route channel (denoted by the short blue lines)
If coordinates are available in the appropriate CSV format, then these can be imported via the import button. Similarly, a defined client scale can be exported.
When creating a client scale, accurate coordinates must be provided by the client as incorrect points could result in a scale not following the Asset/Fiber Route as intended.
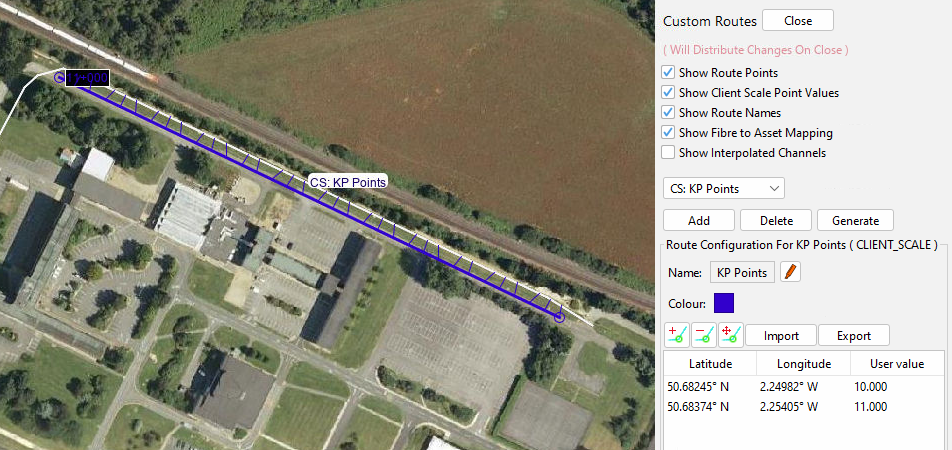
Client Scale with asset mapping enabled
Generating a Client Scale Using Customer Coordinates
In most cases, operators would use the 'Add' button to create a Client Scale, and import customer-generated coordinate positions. However in some cases the resolution/accuracy of these coordinates may to too poor to follow the required Detector Route as intended. In this scenario, the 'Generate’ option can be used that will generate a Client Scale that will fill any gaps with Detetor Route coordinates between customer-generated coordinates.
To generate a Client Scale using Customer coordinates, press the ‘Generate’ button. This will open a dialogue in which the name, colour and parent Detector Route can be supplied. Ensure that the ‘FromFile’ tab is selected and that the customer CSV file has been selected. The OPS’s this Client Scale should apply to also needs to be selected, and any spurs should be removed from consideration.
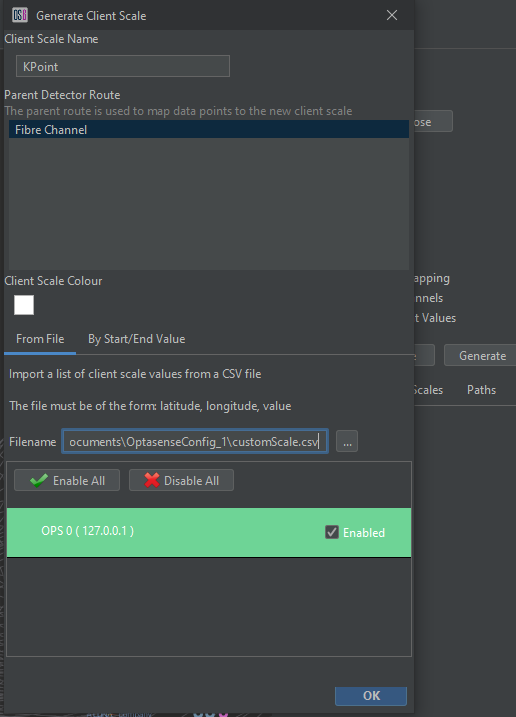
Generate the client scale using customer coordinates
When the OK button is pressed, a Client Scale will be created using a combination of customer and interpolated coordinates.
A generated scale should be checked to ensure that it provides the expected mapping.
Suppression
There are three suppression methods that can be applied to the system to control how it reacts when faced with the following alert scenario. To access the suppression feature, from the toolbar select Configure and then Suppression.

Detector Suppression
Zone Suppression
A zone can be applied to areas and detector instances turned off where nuisance alerts are being generated by a known signal source. For example, a generator within a secure compound is producing a signal like manual digging. A zone is applied to the area and the manual digging detector instance is turned off. Therefore, no alert will be generated in that area for manual digging activity.
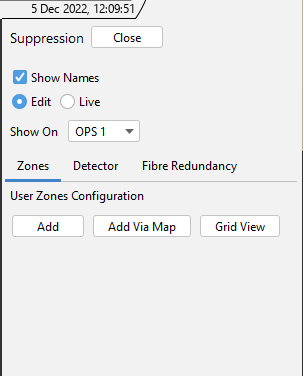
There are 2 ways a zone can be created.
- From the detector suppression configuration panel, select Add Via Map. A prompt will appear instructing the user to draw an area on the map.
- The second way is to select Add from the detector suppression configuration panel.

Left - Creating Area Options / Right – Drawing Area on Map.
The next window enables the user to choose what detector instances will be suppressed. By default, all instances will be selected. Deselect any detectors that don't need to be suppressed. Notice below, the channel range, OPS number and colour representing the zone can be edited. Select apply to make the zone active.
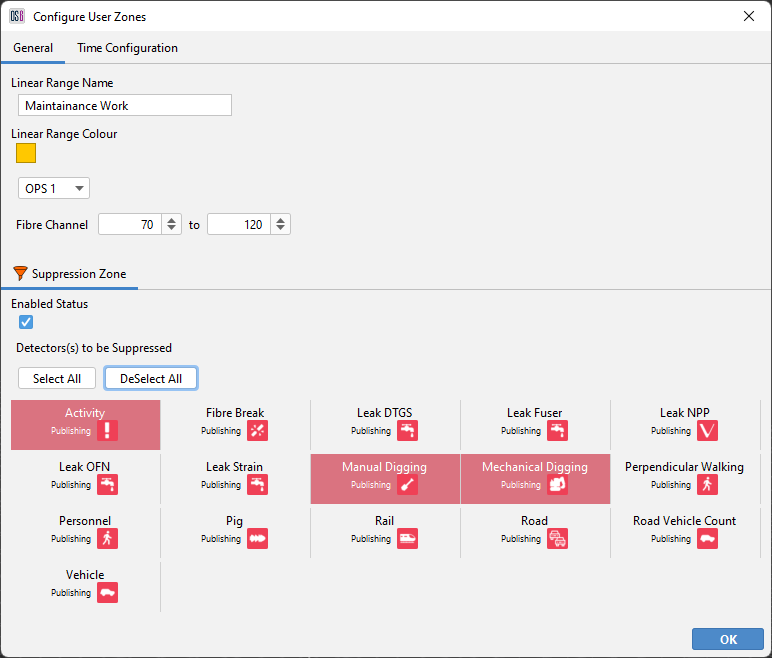
Zone Conditions
Detector Suppression
A detector suppression rule can be applied to allow a generated alert to override (or suppress) other alerts that may be created by the same signal source. For example, a PIG is running through the pipeline and is generating a similar signal source to NPP. Creating a rule where PIG is the suppressor and NPP is the suppressed, means only PIG alerts will be generated.
To create a rule, start by selecting the detector tab from the detector suppression configuration panel. Now select Add.
Add Detector Suppression Rule
There are several options the user can use to aid the configuring of the rule.
The number below explain what can be configured to make up a rule.
- Select how many OPS the rule is to cover
- The alert type of the suppressor
- The alert type(s) to be suppressed
- The hold time is the amount of time that an alert will be held while the system checks for a suppressor alert. This allows the software time to detect another overarching issue that may be causing the original nuisance alert.
- Can be used to increase the extent of the suppression area from the start/end channels of the alert or from the alert centre channel.
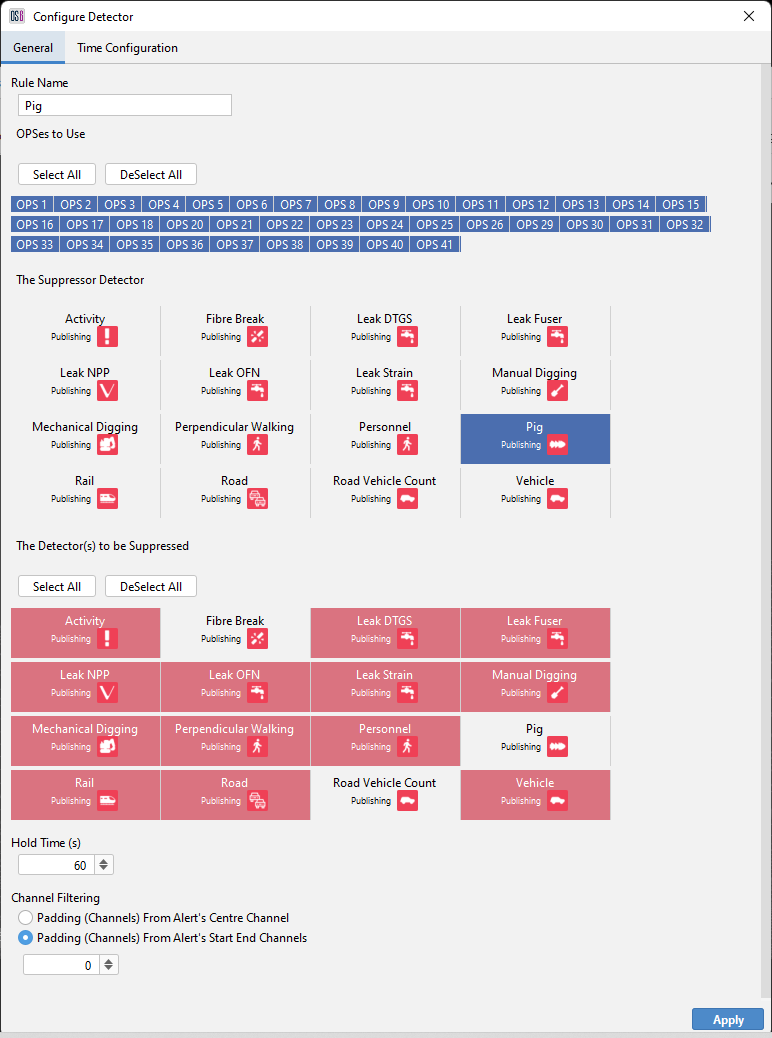
Configuring Detector Suppression Rule
OPS Redundancy Suppression
OPS suppression is used to provide redundancy to two separate OPS's that are covering the same fibre route with one fibre 'suppressing' alerts on the other.
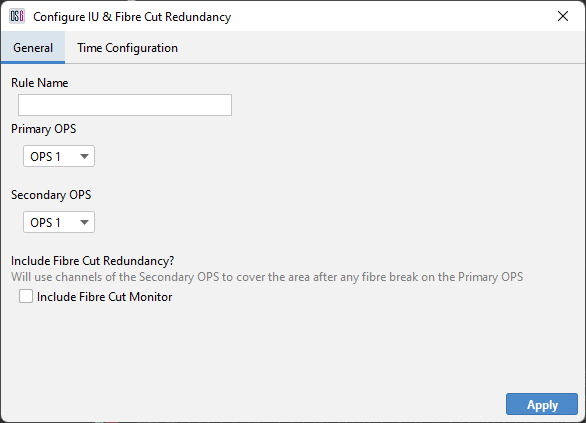
Creating OPS Redundancy Suppression Rule
Suppression Live View
To view live suppression events, they can be observed from the detector suppression configuration panel and map display. To enable this function, select live and toggle the required suppression view or leave as default (Draw All).
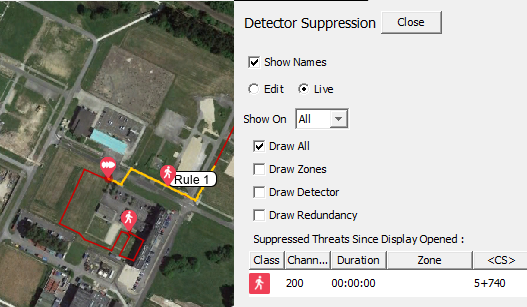
View Suppression Rules
Linear Ranges
It is possible to create a range of channels and associate one or more attributes to it:
- Suppression
- Alert Tags
- Waterfall Frequencies
As per Suppression (see above), a ‘Linear Range’ of Channels can be created and have assigned one or more of the above
Zone Suppression
For details, please see Suppression
Alert Tags
A continuous set of fibre channels can be assigned to have a named ‘Alert Tag’. E.g. when an OptaSense Alert is created within this channel range, it will have the named ‘Alert Tag’ added to the Alert details. This then can be used by a 3rd Party System to identify this location and for example, pan a Camera to this location.

Alert Tag
In the above example, the ‘Entry Gate’ to a perimeter covers Channels 30 to 60. Any Alerts created within these Channels will have ‘Entry Gate’ as the Alert Tag within the Alert Details
Waterfall Frequencies
A continuous set of Fibre channels can be assigned to have user-defined min/max Frequencies. These frequencies do not have any impact on the Detectors. These frequencies only affect the Waterfall display, allowing an Operator to visualize the data for a different set of Frequencies
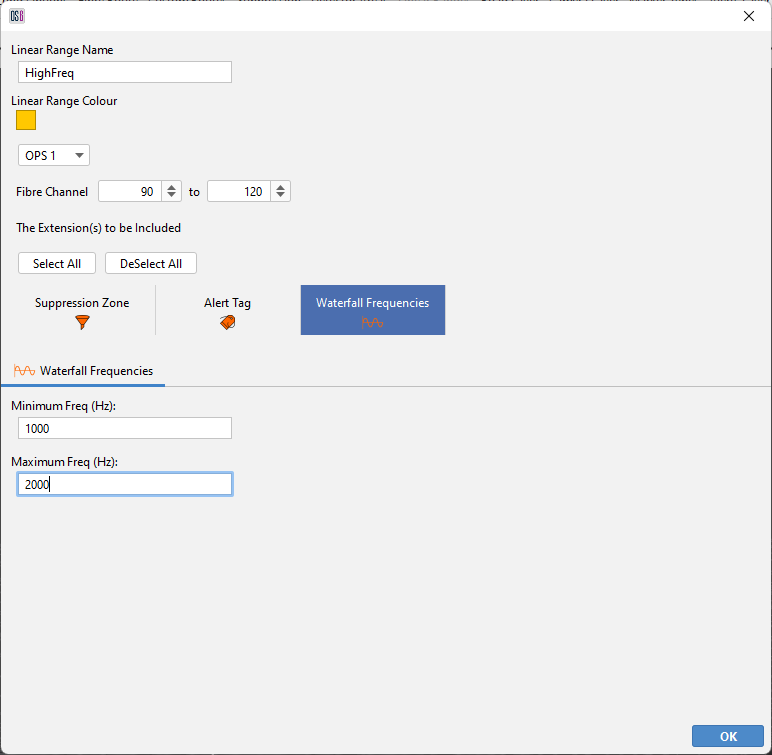
Waterfall Frequencies
Periodic Time Options
Linear ranges can be setup to become active or inactive at certain times/dates using Periodic Times. Periodic Time options are applied per attribute, however only the ‘Zone Suppression’ attribute is supported currently. Below highlights the options available:
Expiry Based Option
Set the attribute to become active/inactive when an expiry time has been reached.
Time Range Based Option
Set the attribute to become active/inactive per day, within a time range (hour/min precision).
Month Based Option
Set the attribute to become active/inactive for certain months out of the year.
Hour Based Option
Set the attribute to become active/inactive for certain hours throughout each day.
Days of The Week Based Option
Set the attribute to become active/inactive for certain days throughout each week.
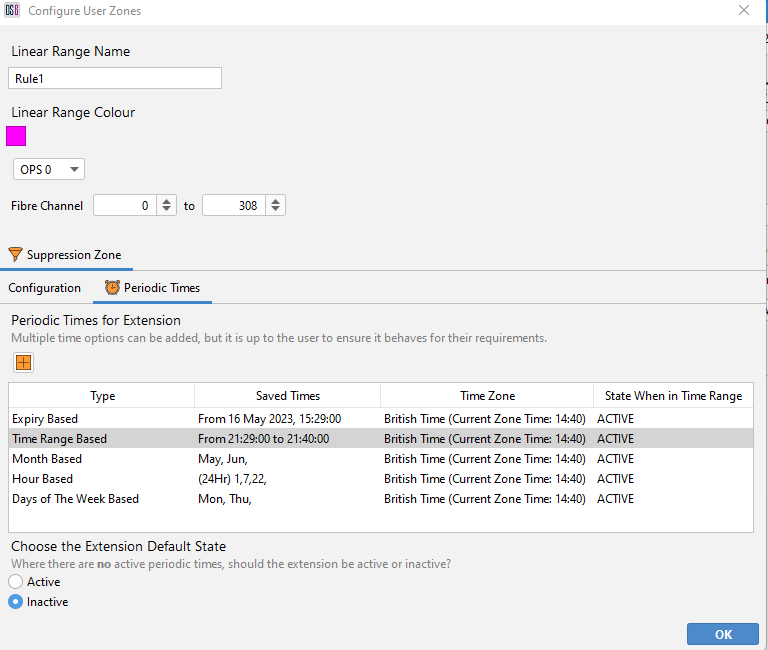
Periodic Times for Suppression Attribute
Multiple Periodic Time options can be added to an attribute, but it is up to the user to ensure it behaves for their requirements. Periodic Times also do not need to be adjusted for daylight savings.
Area of Interest
The area of interest feature enables the user to view all generated alerts within a specified area and time period. What's useful about this feature is it will display all alerts in a summarised fashion irrespective of whether they were acknowledged or dismissed.
From the toolbar, select Configure and then Area Of Interest. A window will appear to the right of the map display.
Configuring Area Of Interest
Select Add to choose between drawing the area by channel range or K point. Now draw the required area on the map and when prompted name it appropriately.
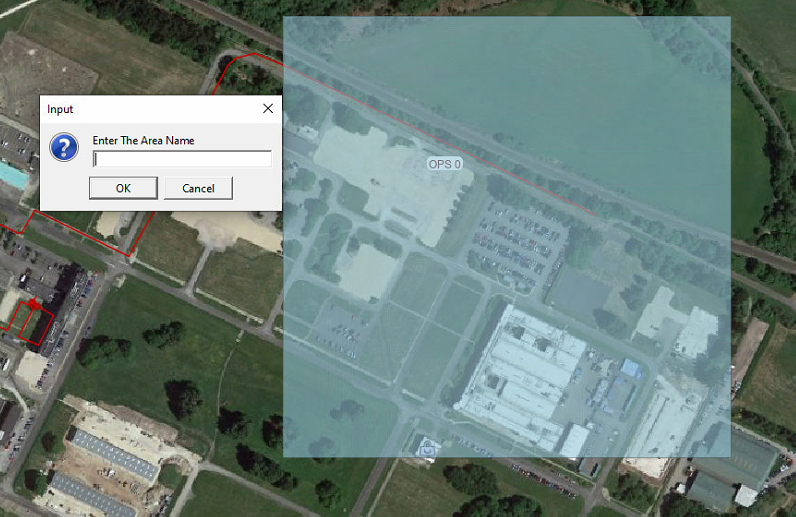
Selecting Map Window
Multiple areas can be created, and their conditions edited at any time. Select Edit to change the following setting.
- Duration: is the amount of days the system will retain alerts.
- Start / End OPS: enable the area to span over two OPS's.
- Remove: will delete a selected area.
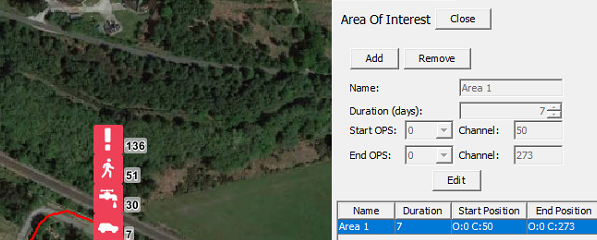
Editing Area
To toggle on and off an Area of Interest showing on the map display, from the toolbar select display and check/uncheck as required.
Toggle Area Of Interest View
Complex Routes
Complex routes allow the user to choose the exact area of fibre they want to apply a zone or suppression area to. This is very useful when dealing with lengths of fibre that pass over each another, loop back on themselves or are connected to separate OPS's. When using complex routes, the software detects the exact OPS channels of the fibre, shown as 'Solution 1' and if possible, offers multiple solutions as seen in Error! Reference source not found..
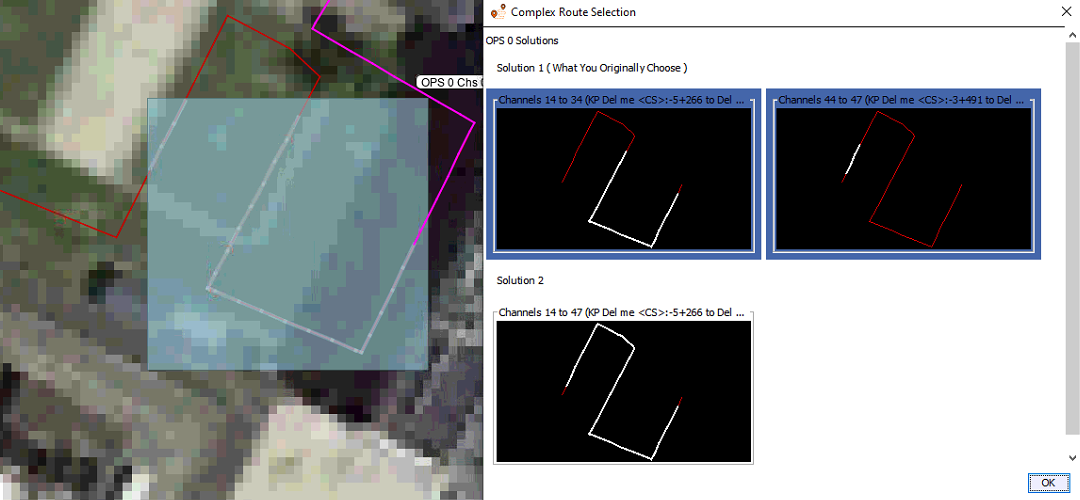
Example complex route solutions
Zoom Areas
A feature added in OS 6.5 is the ability to zoom in user specified areas on the map and display them on the screen at a larger size than their geographical coverage would normally require. This allows, for example a block valve station on a long pipeline to be visible to the operator without having to zoom tightly in on the area, or (as was the only option in earlier versions of the software) having to artificially make the block valve station larger than its actual size in order for it to be visible. This means that alert locations (latitude and longitude) will be correct, where previously with an artificially large area they would not have been correct
Creating a Zoom Area
To create a Zoom Area select the Zoom Area icon from the side bar on the right side of the map window
The Zoom Areas side panel icon
Click the “Add Zoom Area” button and the click and drag on the map in order to create an area around a section of the fibre route to be magnified. Ensure that only the area to be magnified is included.
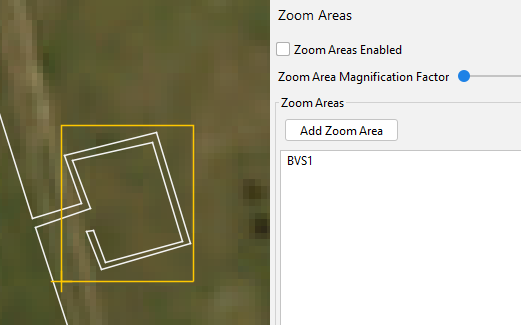
Newly created zoom area
Next, right-click on a location within the newly created area and select “Set Zoom Area Origin” on the point from which the magnification of the area will happen. Everything within the area will be stretched away from this point.
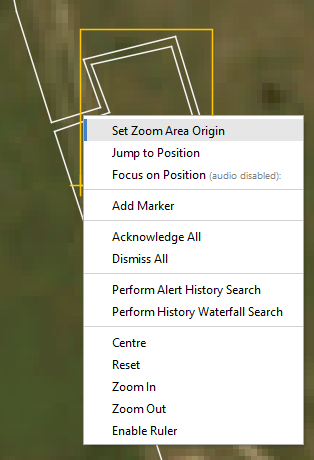
Set zoom area origin
For example on a block valve station, this should be at the point that the fibre leaves and rejoins the pipeline, as shown below
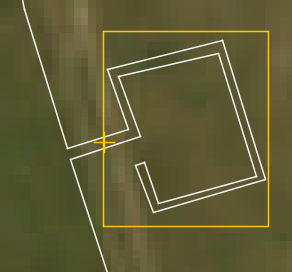
Zoom area origin set as recommended
Finally, the Zoom Area magnification can be enabled and the amount of zoom selected with the sider on the side bar. All items drawn within the area will be zoomed into, this includes the background map image and the size of the blue channel coverage circles.
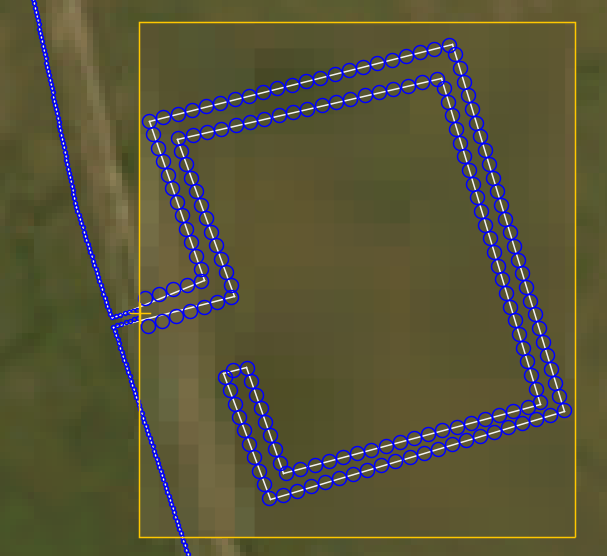
The area zoomed in showing the enlargement of the channel sizes
Final Settings Adjustments
Location and mapping of IU, server and processor nodes logs
All the IU and processor node logs are located on the server node for the system. All the information is present in the System Health feature and the logs can be accessed from there.
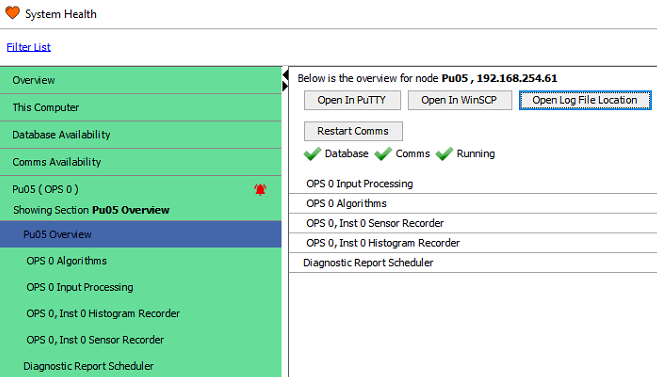
Location of 'Open Log File Location' dialog in System Health
Additionally, this can be accessed via a mapped network drive.
On the CU, open a windows explorer window and select "Map network drive" (displayed on the top toolbar). This will open the "Map Network Drive" window within this window select drive Z and enter the IP address of the server followed by the folder name "logs". The right hand side shows the log files location opened.
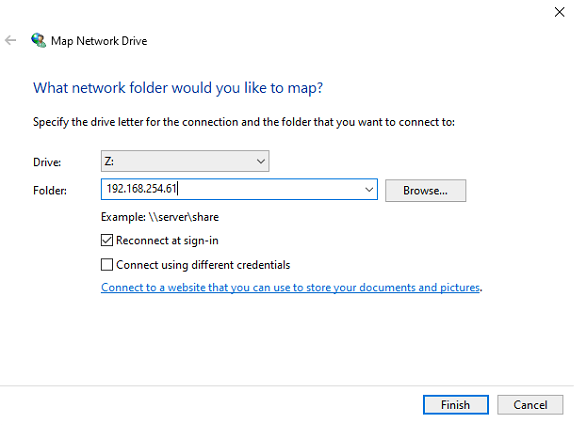
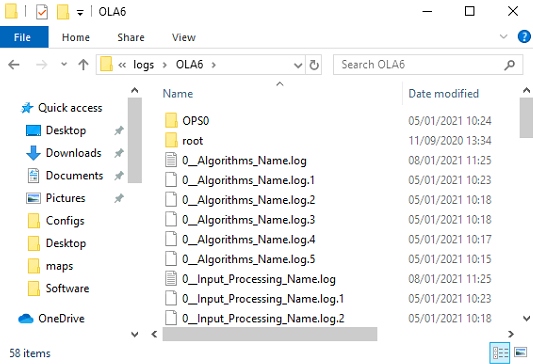
Mapping Network Drive to Server Logs
Location of the CU logs
The CU logs are located on the CU. There is a shortcut to find the location, by left-clicking on the OptaSense software toolbar you can then press F9 and the windows explorer will automatically open at the log location. For information, the full address of the logs is C:\Users\Admin\AppData\Local\OptaSense\OLA6. However, this needs to be typed into the windows explorer toolbar as the folder is hidden so can't be found by just navigating to it.
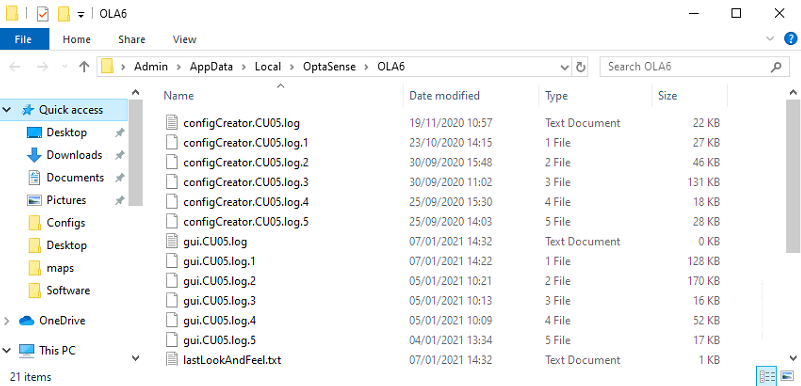
Location of Windows Background tasks logs
A number of OptaSense tasks are run in the ‘Background’ on the CUs (such tasks to to do with re-sizing the System). The location of these logs are on the specific CU
C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\OptaSense\OLA6
Location of Database logs
The logs associated with the Cassandra Database can be found on the Processing Units, as each PU has an instance of Cassandra running on it. To access/view these logs, it is recommended to use ‘putty’ or ‘WinSCP’. The location is:
/var/log/cassandra/system.log
The Homepage
Numerous hardware items within the OptaSense system have web interfaces which enable a lot of configuration changes to be made. All of these are linked to a homepage that is custom-built for each project.
The pieces of equipment that are linked through the homepage are:
- All server and processor nodes (PS, DPS, PU and DPUs) have the IPMI enabled.
- All desk mounted Netgear switches
- All ECPSs
- Dry contact moxas
- SDS for any SMS facility.

OptaSense CU Homepage
Control Unit - shared modification record.
Each CU should also have access to the modification record. To do this:
- Add another folder on the C: Drive of the primary CU entitled the 'Modification record'. Add the modification record from huddle.
- On each CU, create a shortcut on the desktop entitled 'Modification record' and point the CU to the correct location of the 'Modification record' folder on the primary CU
Setting up the Fibre route
The fibre route details that are supplied by the customer need to separate per OPS and placed in a .csv file. This can be achieved via Microsoft Excel, two columns need to be populated, the left for the Latitude values and the right for the longitude values. Once one file has been created for each OPS this needs to be saved as CSV files.
Lat/Long CSV file
To import these values into the OptaSense software the following instructions need to be followed:
- Open the OptaSense software
- Open a Map display
- Select Configure – Fibre Layer
- Click on Edit Installation. Click OK to acknowledge the warning about switching of the algorithms.
Edit Fibre Route Installation
- Select OPS 0 from the OPS drop down box
- Click on import, then locate the .csv file saved with the OPS 0 Lat/Long positions
- Ensure "File contains Lat/Long coordinates" and click OK within the "Select CSV File Type"
- Select "Save" to save the changes
- Follow steps 5-8 for all other OPS'
Advanced GUI Tools
Surveillance Waterfall
The surveillance waterfall enables users to view live acoustic sensor data in graphical format. Activities, as they occur, can be observed through the display, and tools can be used to analyse their source in better detail. To access the waterfall, from the toolbar, select Live Analysis and then Waterfall.
Opening Surveillance Waterfall
Waterfall Options
There are several options that can be used to customise the appearance or aid analysis using the waterfall:
- OPS – OPS Waterfall Selection
- X-Axis – Allows the X-axis scale to be changed to a configured Client Scale or Detector Route
- Scaling – Changes the Histogram scaling and colour values
- General –
- Use Whitened Source – switches between regular and whitened waterfalls
- Track Alerts on Waterfall – determines whether alerts are tracked on the waterfall
- Change Default Frequency Band – Allows the waterfall frequency band to be altered
- Right Click on Waterfall - Allows access to rate, interrogation options and mouse mode options (speed check, creating areas/zones)
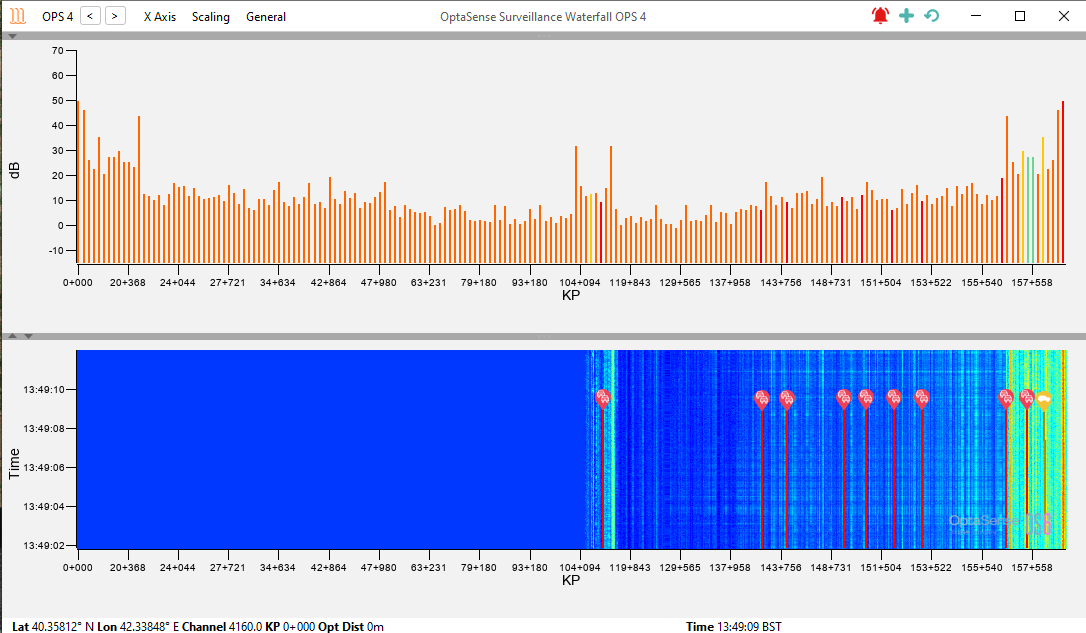
Waterfall Options
Waterfall Frequencies
Another feature of the waterfall display window is the ability to display specific frequency bands. Note that this frequency band selection does not affect the frequencies utilised within the detectors, nor will it modify the sensitivity of the system. This will, however, modify the histogram data when viewed on the waterfall in addition to any subsequent histogram rolling recorder files.
The frequency band used for the waterfall display can be altered by selecting General> Change Default Frequency Band from the drop-down bar at the top of the waterfall. This will open the dialogue box, as shown
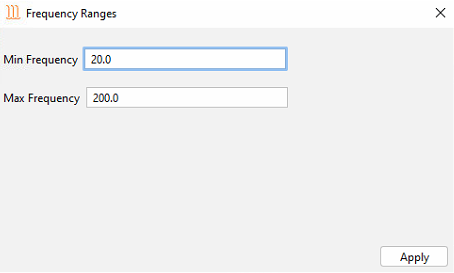
Waterfall Frequency Ranges dialogue box
The default frequency range for the waterfall display is 20 to 200 Hz. This can be tailored on each system to help identify different events.
Live Frequency Analysis window
The Frequency Analysis window enables the user to carry out frequency analysis on the live waterfall. To access this feature, from the toolbar select Live Analysis and then Frequency analysis.
Opening Frequency Analysis Window
The frequency analysis panel displays fibre channels in the x-axis and frequency in the y axis.
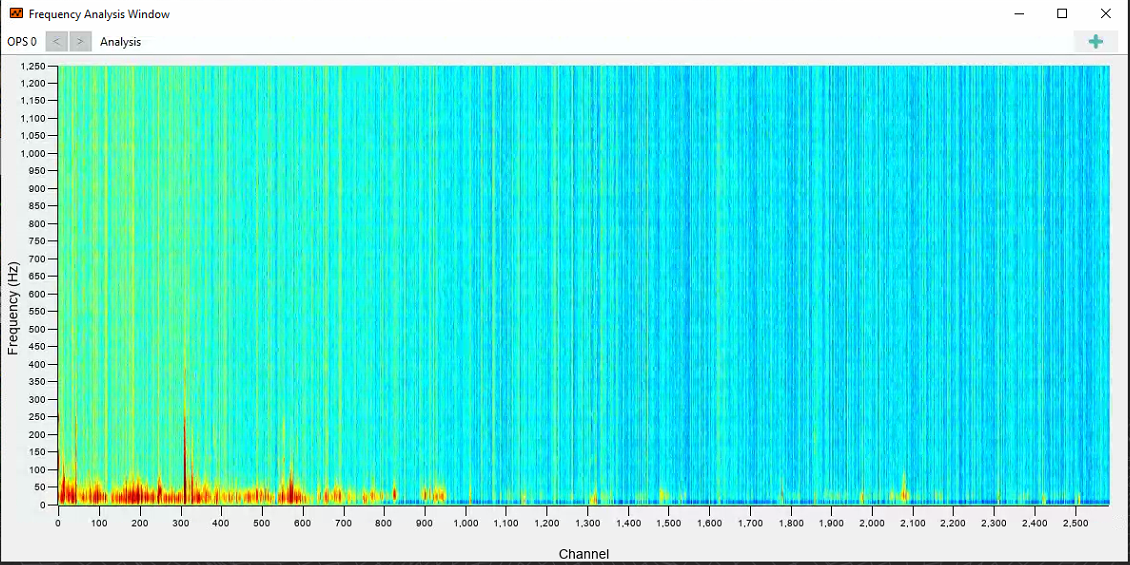
OPS Frequency Analysis Window
Using the menu bar options, the user can change the selection of OPS data to display and by opening the Analysis>Settings dialogue (Error! Reference source not found.) the colour scaling and the decay rate of the data can be changed.
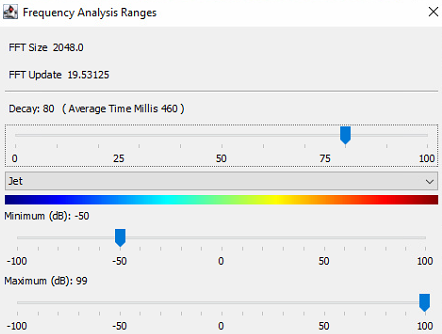
Frequency Range Adjustment
Record and Replay
Record & Replay enables live sensor data to be recorded and replayed later. Note, only trained user accounts have access to this feature. From the toolbar, select Record & Replay.
Selecting Record & Replay
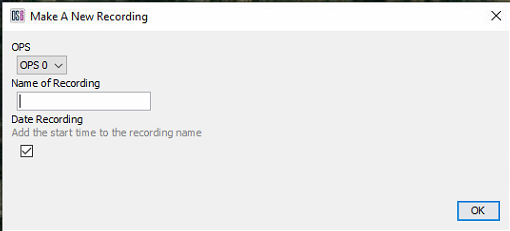
Recording
From the main Record & Replay menu, select the required OPS (top left), then Start New Recording. Fill out the required details, for example, the activity and channel number (Man Dig CH2000). Selecting OK will start the recording. To stop it, right-click on the running recording and select stop.
Record/Replay Window
While recording, if an event of interest occurs, notes can be added to the recording to mark the event. Right-click on the recording and select Add Event. Fill out the text field with the required details and select OK.
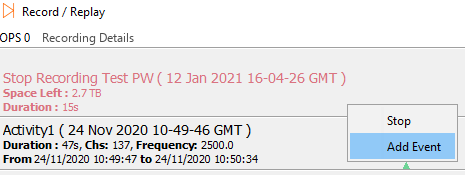
Left – Add Event to Recording / Right – Giving Event Description
Replay
To replay a recording, whilst in the Record & Replay window, right-click of the required recording and select Play.
Replaying a recording will prevent the processing of live data. Similarly, the rolling recorder processes will record the replaying data
A window will appear where the user can alter the replay parameters:
- Loop – Automatically replay the recording once it's finished
- Play With Current Time – Plays the recording as if it were in real current time. Unchecking it will replay the recording with its original time/date
- Start / End Fields – Enables the start and end time to be edited, which is useful for skipping to certain parts of a recording.
When a replay is running, events can be added by rightclicking on the recording in replay and selecting ‘Add Event’.
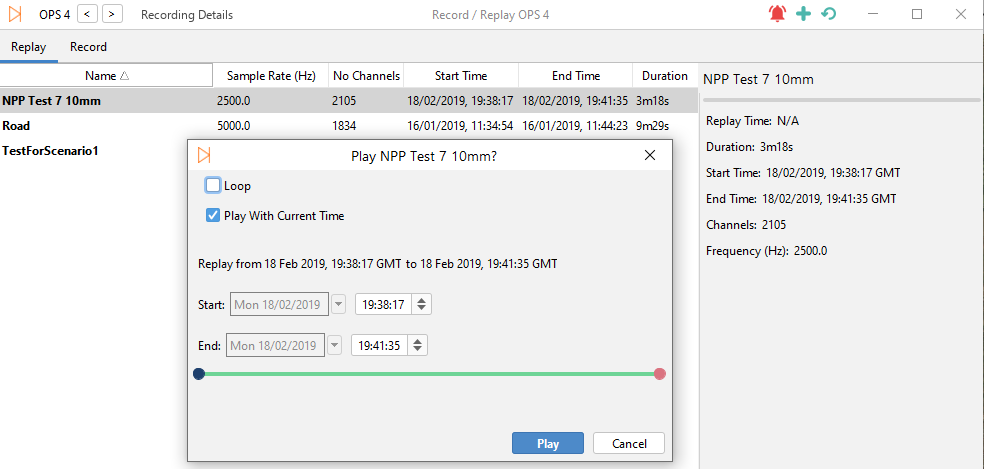
Left – Play Recording / Right – Recording Replay Properties
Manual Record Path
The manual record path is by default. This shouldn't need changing; however, it can be done so by selecting Recording Details and then Change Record Path whilst in the Record & Replay window.
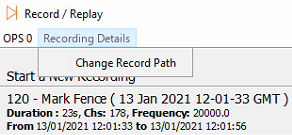
Change Record Path
System Area Lockdown
There are certain areas within the system that are locked down to prevent unwanted changes being made to them. Only those with SuperUser Access can enter a code and unlock them.
Time-Based One-Time Password (Access Code)
In order to elevate to a superuser, an access code will need to be entered when logging into the system. To do this, launch the software and at the login page check Log In As Super User.
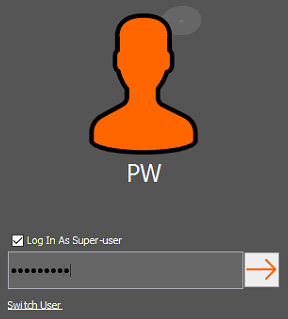
Entering Password
The window will change and ask the user to enter a one-time code. For information in relation to obtaining the code, refer to the next section.
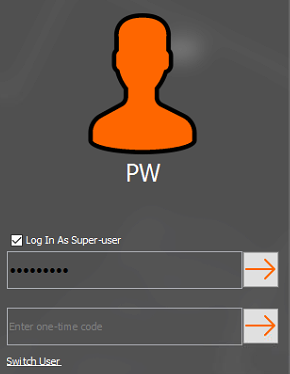
Entering One-time Code
Forgotten Password (Superuser)
In the case a superuser cannot remember their password, the password can be reset. This can be done from the login page by using the ‘Forgot Password’ link. This link is only available for superusers. If non-superusers have forgotten their password, a superuser would need to reset it in the Account Management display.
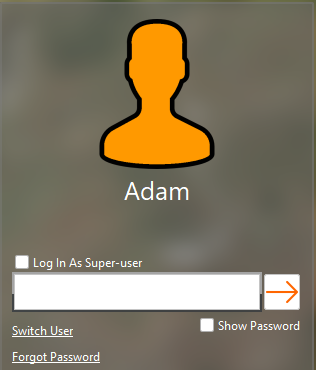
Forgot Password Link
When resetting the superuser password, the One-Time Password (Access Code) will need to be entered in along with the new password.

Forgot Password Display
If a valid One-Time Password (Access Code/TOTP) is entered along with a valid password that conforms to the complexty requirements, the password will reset.
OptaSense Authorisation Server
Firstly, the user will need to access the OptaSense Authorisation Server. This can be done using any typical internet browser.
In the search bar, enter the following address: https://auth.optasense.com
Authorisation Server Log In
Each user will have log in details that will give them access to the server.
Once the correct login details have been entered, they will be taken to the main homepage of the authorisation server.

Authorisation Server Homepage
In the top left of the screen, click on the menu drop down box and select Groups.

Group Selection
A software licence must have already been created. The generated access code links to the MAC address of the system that requires access. An access code generated using a different licence group will not work. The created licence can then be found and selected within the Groups drop-down window.
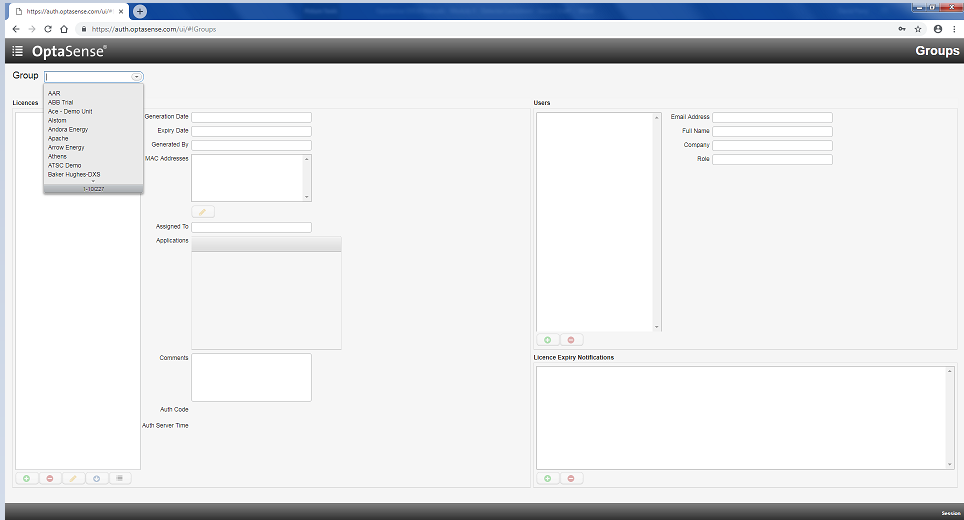
Dropdown Window Group Licence Selection
Having selected the appropriate group from the list, the authorisation server will now display the different licences that relate to the project system. Some systems may have multiple licences attached to their group. This is dependent on the number of CUs within the system.
Selecting the appropriate licence provides the user with an Auth Code. This is the code that needs to be entered as the one-time code. As stated, the access code will regenerate every 30 seconds. A countdown timer, as well as the current Authorisation Server time in UTC, will be displayed. The time displayed allows the user to make a comparison between the server and the CU being worked on. Once the timer has reached zero, the code displayed will expire and a new code will be generated. The code must be entered within 10 minutes of generation.
Once the access code has been entered, the user will now have full system access.
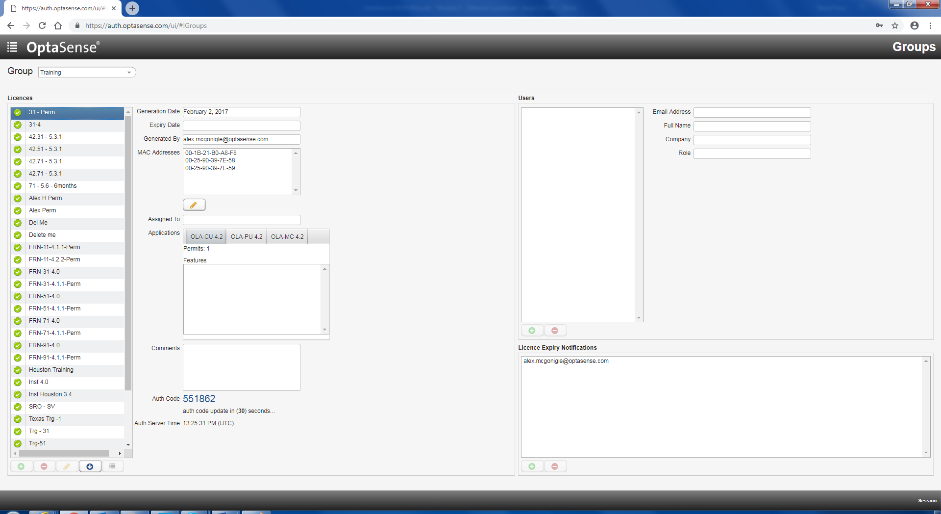
Generated Access Code
Contacting an Authorised OptaSense Engineer
If a user requires Super User access and they do not have access to the OptaSense Authorisation Server due to the lack of a reliable internet connection, then it will be necessary to contact an authorised person from OptaSense or to arrange a support contract that includes code access.
Once in contact with an authorised person, the onsite user will need to provide details of the project so that the correct Group and Licence can be found.
Detector guidance for local administrators
As a Trained User, it is possible to modify the detector settings. The detectors are configured during the initial commissioning and SAT stages of installation in line with the clients' Threat Profile. The detectors are updated during IOC-FOC improving the overall alert rate and reducing nuisance alerts. Note that the sensitivity of the system is dependent on environmental factors such as ground types and seasonal variations.
Any changes to the detectors should be carried by trained operators
OptaSense Support Portal
If you have a support contract and would like to raise a request, you can contact us at http://support.optasense.com
For enquiries regarding obtaining a support contract, please also use the address above.